This is a preprint.
De novo design of drug-binding proteins with predictable binding energy and specificity
- PMID: 38187746
- PMCID: PMC10769398
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.12.23.573178
De novo design of drug-binding proteins with predictable binding energy and specificity
Update in
-
De novo design of drug-binding proteins with predictable binding energy and specificity.Science. 2024 Apr 5;384(6691):106-112. doi: 10.1126/science.adl5364. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Science. 2024. PMID: 38574125 Free PMC article.
Abstract
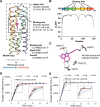
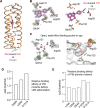
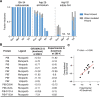
The de novo design of small-molecule-binding proteins has seen exciting recent progress; however, the ability to achieve exquisite affinity for binding small molecules while tuning specificity has not yet been demonstrated directly from computation. Here, we develop a computational procedure that results in the highest affinity binders to date with predetermined relative affinities, targeting a series of PARP1 inhibitors. Two of four designed proteins bound with affinities ranging from < 5 nM to low μM, in a predictable manner. X-ray crystal structures confirmed the accuracy of the designed protein-drug interactions. Molecular dynamics simulations informed the role of water in binding. Binding free-energy calculations performed directly on the designed models are in excellent agreement with the experimentally measured affinities, suggesting that the de novo design of small-molecule-binding proteins with tuned interaction energies is now feasible entirely from computation. We expect these methods to open many opportunities in biomedicine, including rapid sensor development, antidote design, and drug delivery vehicles.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing financial interests A.A. is a co-founder of Tango Therapeutics, Azkarra Therapeutics, Ovibio Corporation and Kytarro, a member of the board of Cytomx and Cambridge Science Corporation, a member of the scientific advisory board of Genentech, GLAdiator, Circle, Bluestar, Earli, Ambagon, Phoenix Molecular Designs, Yingli, ProRavel, Oric, Hap10 and Trial Library, a consultant for SPARC, ProLynx, Novartis and GSK, receives research support from SPARC, and holds patents on the use of PARP inhibitors held jointly with AstraZeneca from which he has benefited financially (and may do so in the future).
Figures


References
-
- Röthlisberger D., Khersonsky O., Wollacott A. M., Jiang L., DeChancie J., Betker J., Gallaher J. L., Althoff E. A., Zanghellini A., Dym O., Albeck S., Houk K. N., Tawfik D. S., Baker D., Kemp elimination catalysts by computational enzyme design. Nature 453, 190–195 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Yang W., Lai L., Computational design of ligand-binding proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 45, 67–73 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
