Vitamin C - a scoping review for Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2023
- PMID: 38187788
- PMCID: PMC10770653
- DOI: 10.29219/fnr.v67.10300
Vitamin C - a scoping review for Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2023
Abstract
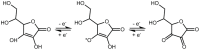
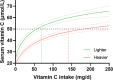
Vitamin C has multiple metabolic functions in the body, but the available information on the exact relationship between these functions and the intake necessary to maintain them is very limited. However, most attempts to objectively measure adequacy of vitamin C status, including, for example, replacement of metabolic turnover, chronic disease prevention, urinary excretion, and saturation of immune cells and body compartment, currently point toward 50 µmol/L as a reasonable target plasma concentration. As a strong correlation between body weight and vitamin C status exists, recommended intakes (RIs) for other age groups may be extrapolated from the adult RI based on weight. However, as body weights above 70 kg are becoming increasingly common - also in the Nordic region - an RI of 140 mg/day for individuals weighing 100 kg or more should be considered to compensate for the larger volume of distribution. Finally, smoking continues to be a common contributor to poor vitamin C status; therefore, it is proposed that people who smoke increase their daily vitamin C intake by 40 mg/day to compensate for the increased metabolic turnover induced by smoking.
Keywords: antioxidants; ascorbic acid; nutrition recommendations; vitamin C.
© 2023 Jens Lykkesfeldt and Anitra Carr.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have not received any funding or benefits from industry or elsewhere to conduct this study.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Estimation of Vitamin C Intake Requirements Based on Body Weight: Implications for Obesity.Nutrients. 2022 Mar 31;14(7):1460. doi: 10.3390/nu14071460. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35406073 Free PMC article.
-
New Reference Values for Vitamin C Intake.Ann Nutr Metab. 2015;67(1):13-20. doi: 10.1159/000434757. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Ann Nutr Metab. 2015. PMID: 26227083
-
Factors Affecting the Vitamin C Dose-Concentration Relationship: Implications for Global Vitamin C Dietary Recommendations.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 29;15(7):1657. doi: 10.3390/nu15071657. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37049497 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin B12 - a scoping review for Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2023.Food Nutr Res. 2023 Nov 8;67. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v67.10257. eCollection 2023. Food Nutr Res. 2023. PMID: 38084149 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin A - a scoping review for Nordic nutrition Recommendations 2023.Food Nutr Res. 2023 Nov 7;67. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v67.10229. eCollection 2023. Food Nutr Res. 2023. PMID: 38686175 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular Pharmacology of Vitamin C and Relevance to Health and Obesity-A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7523. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147523. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex Differences in Vitamin Metabolism and Their Role in Oxidative Stress Regulation and Cardiometabolic Health.Nutrients. 2025 Aug 20;17(16):2697. doi: 10.3390/nu17162697. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40871724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the potential of selenium nanoparticles and fabricated selenium nanoparticles @vitamin C nanocomposite in mitigating nicotine-induced testicular toxicity in rats.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Sep 30;13(5):tfae154. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae154. eCollection 2024 Oct. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39359714
References
-
- Medical Research Council (Great Britain) Accessory Food Factors Committee . Vitamin C requirement of human adults. London: Her Majesty’s Stationery Office; 1953.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

