Management and outcomes of superficial vein thrombosis: a single-center retrospective study
- PMID: 38187826
- PMCID: PMC10770555
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpth.2023.102263
Management and outcomes of superficial vein thrombosis: a single-center retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Guidelines suggest but cannot recommend the optimal management of superficial vein thrombosis (SVT).
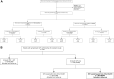
Objectives: To identify the prevalence of asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis (DVT) at the time of SVT diagnosis, and to report the treatment and 3-month complications of patients with only SVT more than 3 cm from deep vein junction (or unknown distance).
Methods: We performed a single-center retrospective review of patients referred to the Ottawa Hospital thrombosis unit with ultrasound (US)-diagnosed SVT, and followed patients with only SVT for 3 months.
Results: Three hundred sixteen patients with SVT were included. Of the 218 patients without DVT symptoms at presentation, 19 (8.7%; 95% CI, 5.7%-13.2%) were found to have asymptomatic concomitant DVT (11 proximal and 8 distal), and 45 (20.6%) had SVT within 3 cm of the saphenofemoral or saphenopopliteal junctions. Among the 192 patients diagnosed with SVT only, we observed 3-month thrombotic complications in 56 (29.2%; 95% CI, 23.2%-36.0%) patients, with a total of 69 events: 11 (5.7%) DVTs, 2 (1.0%) pulmonary embolisms, 37 (19.2%) SVT extensions, and 19 (9.8%) SVT recurrences. Eighty-two percent (9/11) of the 3-month DVT and pulmonary embolism events occurred in patients who initially received conservative management. Therapeutic treatment doses were most effective.
Conclusion: At the time of SVT diagnosis, many patients had asymptomatic DVT and SVT near the deep venous system, supporting the systematic use of initial US in patients clinically diagnosed with SVT. The observed differences in 3-month complication rates, according to the treatment provided, highlight the need for large-scale randomized controlled trials to establish optimal management.
Keywords: anticoagulant; deep vein thrombosis; pulmonary embolism; ultrasound; venous thromboembolism.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Superficial venous thrombosis and compression ultrasound imaging.J Vasc Surg. 2012 Oct;56(4):1032-8.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2012.03.014. Epub 2012 Jul 24. J Vasc Surg. 2012. PMID: 22832262
-
Prevalence of cancer in patients with superficial vein thrombosis and its clinical importance.J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2022 Jan;10(1):26-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2021.05.006. Epub 2021 Jun 2. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2022. PMID: 34089942
-
Long-term risk of venous thromboembolism recurrence after isolated superficial vein thrombosis.J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Jun;15(6):1123-1131. doi: 10.1111/jth.13679. Epub 2017 May 5. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28317330
-
Management of superficial vein thrombosis.J Thromb Haemost. 2015 Jul;13(7):1175-83. doi: 10.1111/jth.12986. Epub 2015 May 25. J Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 25903684 Review.
-
Epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment and management of superficial-vein thrombosis of the legs.Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2012 Sep;25(3):275-84. doi: 10.1016/j.beha.2012.07.005. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2012. PMID: 22959544 Review.
Cited by
-
Just the facts: diagnosis and management of superficial thrombophlebitis in the ED.CJEM. 2025 Feb;27(2):96-99. doi: 10.1007/s43678-024-00818-w. Epub 2025 Feb 6. CJEM. 2025. PMID: 39912862 No abstract available.
-
Treatment of Superficial Vein Thrombosis: Recent Advances, Unmet Needs and Future Directions.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Jul 31;12(15):1517. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12151517. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39120220 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Frappé P., Buchmuller-Cordier A., Bertoletti L., Bonithon-Kopp C., Couzan S., Lafond P., et al. Annual diagnosis rate of superficial vein thrombosis of the lower limbs: the STEPH community-based study. J Thromb Haemost. 2014;12:831–838. - PubMed
-
- Geersing G.J., Cazemier S., Rutten F., Fitzmaurice D.A., Hoes A.W. Incidence of superficial venous thrombosis in primary care and risk of subsequent venous thromboembolic sequelae: a retrospective cohort study performed with routine healthcare data from the Netherlands. BMJ Open. 2018;8 doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019967. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Decousus H., Frappé P., Accassat S., Bertoletti L., Buchmuller A., Seffert B., et al. Epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment and management of superficial-vein thrombosis of the legs. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2012;25:275–284. - PubMed
-
- Decousus H., Quéré I., Presles E., Becker F., Barrellier M.T., Chanut M., et al. Superficial venous thrombosis and venous thromboembolism: a large, prospective epidemiologic study. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152:218–224. - PubMed
-
- van Langevelde K., Lijfering W.M., Rosendaal F.R., Cannegieter S.C. Increased risk of venous thrombosis in persons with clinically diagnosed superficial vein thrombosis: results from the MEGA study. Blood. 2011;118:4239–4241. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

