Mycotoxins from Alternaria Panax, the specific plant pathogen of Panax ginseng
- PMID: 38187879
- PMCID: PMC10769115
- DOI: 10.1080/21501203.2023.2265662
Mycotoxins from Alternaria Panax, the specific plant pathogen of Panax ginseng
Abstract
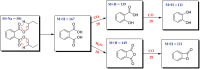
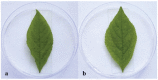
Ginseng black spot, caused by Alternaria panax, is one of the most common diseases of Panax ginseng, which usually causes serious yield loss of ginseng plants. However, the pathogenic mechanism of A. panax has not been clarified clearly. Mycotoxins produced by phytopathogens play an important role in the process of infection. Previous study reported that dibutyl phthalate (DBP) identified from the metabolites of A. panax is a potent mycotoxin against P. ginseng. However, more evidence suggests that DBP is one of the constituents of plasticisers. To identify mycotoxins from A. panax and evaluate their phytotoxicity on the leaves of P. ginseng, different chromatographic, spectral and bioassay-guided methods were used together in this report. As a result, tyrosol (1), 3-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl) propanoic acid (2), and 3-benzylpiperazine-2,5-dione (3) were isolated and characterised from the extract of A. panax, in which compounds 1 and 2 showed phytotoxic activity on ginseng leaves. Furthermore, DBP was confirmed to come from the residue of ethyl acetate through UPLC-MS/MS analysis, and displayed no phytotoxicity on ginseng leaves based on biological experiments. The results in this report first revealed that tyrosol (1), and 3-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl) propanoic acid (2) not DBP were the potent mycotoxins of A. panax.
Keywords: Alternaria panax; Panax ginseng; dibutyl phthalate; mycotoxin; phytotoxic activities.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures

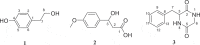



Similar articles
-
ApWD40a, a Member of the WD40-Repeat Protein Family, Is Crucial for Fungal Development, Toxin Synthesis, and Pathogenicity in the Ginseng Alternaria Leaf Blight Fungus Alternaria panax.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Jan 14;11(1):59. doi: 10.3390/jof11010059. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39852478 Free PMC article.
-
Silicon application and related changes in soil bacterial community dynamics reduced ginseng black spot incidence in Panax ginseng in a short-term study.BMC Microbiol. 2019 Nov 26;19(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1627-z. BMC Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31771526 Free PMC article.
-
Ethyl acetate extract from Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer and its main constituents inhibit α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-induced melanogenesis by suppressing oxidative stress in B16 mouse melanoma cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Aug 17;208:149-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Jul 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28689798
-
[Colonization characteristics of endophytic bacteria NJ13 in Panax ginseng and its biocontrol efficiency against Alternaria leaf spot of ginseng].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 May;39(10):1782-7. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25282882 Chinese.
-
An investigation of Panax ginseng Meyer growth promotion and the biocontrol potential of antagonistic bacteria against ginseng black spot.J Ginseng Res. 2018 Jul;42(3):304-311. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2017.03.012. Epub 2017 Apr 21. J Ginseng Res. 2018. PMID: 29983611 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Toxin Production by Alternaria alternata in Black Spot Disease of Chrysanthemum morifolium 'Fubai': Accumulation of Altenuene and Tenuazonic Acid in Flowers.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Apr 5;17(4):181. doi: 10.3390/toxins17040181. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40278679 Free PMC article.
-
ApWD40a, a Member of the WD40-Repeat Protein Family, Is Crucial for Fungal Development, Toxin Synthesis, and Pathogenicity in the Ginseng Alternaria Leaf Blight Fungus Alternaria panax.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Jan 14;11(1):59. doi: 10.3390/jof11010059. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39852478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bietti M, Capone A. 2006. Reactivity and acid-base behavior of ring-methoxylated arylalkanoic acid radical cations and radical zwitterions in aqueous solution. Influence of structural effects and pH on the benzylic C-H deprotonation pathway. J Org Chem. 71(14):5260–5267. doi: 10.1021/jo060678i. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen CQ, Tong LI, Xin-Lian LI, Yun J, Lei T, Peng XU. 2014. Colonization characteristics of endophytic bacteria NJ13 in panax ginseng and its biocontrol efficiency against Alternaria leaf spot of ginseng. China J Chin Mater Med. 39(10):1782–1787. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
