Wheat Ceramide Powder Mitigates Ultraviolet B-Induced Oxidative Stress and Photoaging by Inhibiting Collagen Proteolysis and Promoting Collagen Synthesis in Hairless Mice
- PMID: 38188085
- PMCID: PMC10764234
- DOI: 10.3746/pnf.2023.28.4.418
Wheat Ceramide Powder Mitigates Ultraviolet B-Induced Oxidative Stress and Photoaging by Inhibiting Collagen Proteolysis and Promoting Collagen Synthesis in Hairless Mice
Abstract
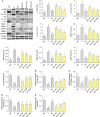
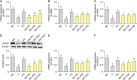
The protective effects of wheat ceramide powder (WC-P) on ultraviolet B (UVB)-induced skin oxidative stress and photoaging in hairless mice were investigated in this study. Moreover, the activities of antioxidant enzymes, inflammation, wrinkle formation-related pathway, and moisturizing capacity were evaluated. Mice were randomly divided into six groups (n=8): normal control (non-UVB irradiation), control (UVB irradiation), L-ascorbic acid [positive control, UVB irradiation with dietary supplementation of L-ascorbic acid at 100 mg/kg/body weight (bw)], WC-P5 (UVB irradiation with dietary supplementation of WC-P at 5 mg/kg/bw), WC-P20 (UVB irradiation with dietary supplementation of WC-P at 20 mg/kg/bw), and WC-P40 (UVB irradiation with dietary supplementation of WC-P at 40 mg/kg/bw). AIN-96G diet and water were supplemented ad libitum, and 100 mL of L-ascorbic acid and WC-P dissolved in water were forcefully administered orally to mice. UVB irradiation resulted in dehydration and wrinkle formation in the dorsal skin of mice. However, WC-P supplementation suppressed. Furthermore, WC-P supplementation enhanced the activites of antioxidant enzymes and expression of transforming growth factor-β receptor I, procollaten C-endopeptideas enhancer protein, hyaluronan synthase, and ceramide synthase 4 and reduced the activation of the inflammation and the c-Jun N-terminal kinase/c-FOS/c-Jun- mediated matrix metalloproteinase pathways. These findings demonstrate that WC-P can protect the skin from UVB-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and photoaging by inhibiting collagen proteolysis and promoting collagen synthesis, thereby promoting skin health.
Keywords: collagen; skin aging; ultraviolet ray; wheat ceramides.
© 2023 The Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
AUTHOR DISCLOSURE STATEMENT The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucocerebroside-Containing Milk Concentrated Powder Suppresses Oxidative Stress and Photoaging in the Skin of Hairless Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 13;11(9):1804. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091804. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139878 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Ceramides Derivatives from the Peach on Skin Function Improvement in UV-Irradiated Hairless Mice.Foods. 2024 Nov 27;13(23):3824. doi: 10.3390/foods13233824. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39682897 Free PMC article.
-
Enzyme-Treated Caviar Prevents UVB Irradiation-Induced Skin Photoaging.Mar Drugs. 2022 Oct 30;20(11):685. doi: 10.3390/md20110685. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36355008 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of the standardized green tea seed extract on UVB-induced skin photoaging in hairless mice.Nutr Res Pract. 2014 Aug;8(4):398-403. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2014.8.4.398. Epub 2014 May 15. Nutr Res Pract. 2014. PMID: 25110559 Free PMC article.
-
Krill Oil's Protective Benefits against Ultraviolet B-Induced Skin Photoaging in Hairless Mice and In Vitro Experiments.Mar Drugs. 2023 Aug 30;21(9):479. doi: 10.3390/md21090479. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37755092 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeting ceramide-induced microglial pyroptosis: Icariin is a promising therapy for Alzheimer's disease.J Pharm Anal. 2025 Apr;15(4):101106. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101106. Epub 2024 Sep 19. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 40256246 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansary TM, Hossain MR, Kamiya K, Komine M, Ohtsuki M. Inflammatory molecules associated with ultraviolet radiation- mediated skin aging. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:3974. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22083974. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bizot V, Cestone E, Michelotti A, Nobile V. Improving skin hydration and age-related symptoms by oral administration of wheat glucosylceramides and digalactosyl diglycerides: a human clinical study. Cosmetics. 2017;4:37. doi: 10.3390/cosmetics4040037. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics4040037. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
