Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of (Artemisinin/Querctin/ Zinc) novel mixed ligand complex with assessment of its potent high antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and antioxidant capacity against toxicity induced by acrylamide in male rats
- PMID: 38188145
- PMCID: PMC10768679
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.15638
Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of (Artemisinin/Querctin/ Zinc) novel mixed ligand complex with assessment of its potent high antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and antioxidant capacity against toxicity induced by acrylamide in male rats
Abstract
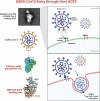
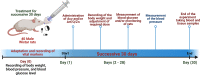
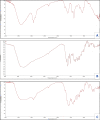
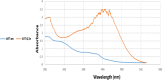
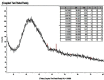
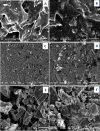
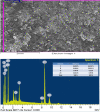
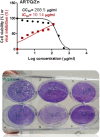
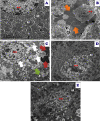
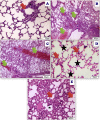
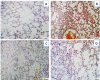
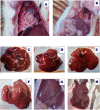
A novel Artemisinin/Quercetin/Zinc (Art/Q/Zn) mixed ligand complex was synthesized, tested for its antiviral activity against coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), and investigated for its effect against toxicity and oxidative stress induced by acrylamide (Acy), which develops upon cooking starchy foods at high temperatures. The synthesized complex was chemically characterized by performing elemental analysis, conductance measurements, FT-IR, UV, magnetic measurements, and XRD. The morphological surface of the complex Art/Q/Zn was investigated using scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM) and energy dispersive X-ray analysis (XRD). The in vitro antiviral activity of the complex Art/Q/Zn against SARS-CoV-2 and its in vivo activity against Acy-induced toxicity in hepatic and pulmonary tissues were analyzed. An experimental model was used to evaluate the beneficial effects of the novel Art/Q/Zn novel complex on lung and liver toxicities of Acy. Forty male rats were randomly divided into four groups: control, Acy (500 mg/Kg), Art/Q/Zn (30 mg/kg), and a combination of Acy and Art/Q/Zn. The complex was orally administered for 30 days. Hepatic function and inflammation marker (CRP), tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-6 (IL-6), antioxidant enzyme (CAT, SOD, and GPx), marker of oxidative stress (MDA), and blood pressure levels were investigated. Histological and ultrastructure alterations and caspase-3 variations (immunological marker) were also investigated. FT-IR spectra revealed that Zn (II) is able to chelate through C=O and C-OH (Ring II) which are the carbonyl oxygen atoms of the quercetin ligand and carbonyl oxygen atom C=O of the Art ligand, forming Art/Q/Zn complex with the chemical formula [Zn(Q)(Art)(Cl)(H2O)2]⋅3H2O. The novel complex exhibited a potent anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity even at a low concentration (IC50 = 10.14 µg/ml) and was not cytotoxic to the cellular host (CC50 = 208.5 µg/ml). Art/Q/Zn may inhibit the viral replication and binding to the angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) receptor and the main protease inhibitor (MPro), thereby inhibiting the activity of SARS-CoV-2 and this proved by the molecular dynamics simulation. It alleviated Acy hepatic and pulmonary toxicity by improving all biochemical markers. Therefore, it can be concluded that the novel formula Art/Q/Zn complex is an effective antioxidant agent against the oxidative stress series, and it has high inhibitory effect against SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Artemisinin; Novel complex; Pandemic; SARS-CoV-2; Transmission electron microscope.
©2024 El-Megharbel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Synthesis and spectroscopic study of novel mixed ligand formula "Artemisinin/Zn" and assessment of its inhibitory effect against "SARS-CoV-2″.Heliyon. 2023 Jun;9(6):e17177. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17177. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37366527 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin/Zinc complex and stem cells: A new drug therapy to ameliorate glycometabolic control and pulmonary dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: Structural characterization and genetic studies.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 4;16(3):e0246265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246265. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33661932 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of lactoferrin-coated zinc nanoparticles on SARS-CoV-2 replication and entry along with improvement of lung fibrosis induced in adult male albino rats.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Aug 1;245:125552. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125552. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37356684 Free PMC article.
-
Potential molecular mechanisms of zinc- and copper-mediated antiviral activity on COVID-19.Nutr Res. 2021 Aug;92:109-128. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2021.05.008. Epub 2021 Jun 13. Nutr Res. 2021. PMID: 34284268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repurposing potential of Ayurvedic medicinal plants derived active principles against SARS-CoV-2 associated target proteins revealed by molecular docking, molecular dynamics and MM-PBSA studies.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 May;137:111356. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111356. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33561649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abo Elmaaty A, Eldehna WM, Khattab M, Kutkat O, Alnajjar R, El-Taweel AN, Al-Rashood ST, Abourehab MAS, Binjubair FA, Saleh MA. Anticoagulants as potential SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors for COVID-19 patients: in vitro, molecular docking, molecular dynamics, DFT, and SAR studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022;23(20):12235. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012235. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abubakar MG, Ukwuani AN, Mande UU. Antihypertensive activity of Hibiscus Sabdariffa aqueous calyx extract in Albino rats. Sky Journal of Biochemistry Research. 2015;4(3):16–20.
-
- Aebi Catalase in vitro. Methods in Enzymology. 1984;105:121–126. - PubMed
-
- Al-Shemary RK, Ranjan KM, Manjeet K, Ashish K, Mohammad A, Hardeep ST, Azaj A, Pranab K, Mohapatra G, Kuldeep D. Synthesis, structural investigations, XRD, DFT, anticancer and molecular docking study of a series of thiazole-based Schiff base metal complexes. Journal of Molecular Structure. 2023;1275:134676. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134676. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

