Multidimensional Separations in Top-Down Proteomics
- PMID: 38188188
- PMCID: PMC10769458
- DOI: 10.1002/ansa.202300016
Multidimensional Separations in Top-Down Proteomics
Abstract
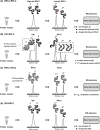
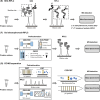
Top-down proteomics (TDP) identifies, quantifies, and characterizes proteins at the intact proteoform level in complex biological samples to understand proteoform function and cellular mechanisms. However, analyzing complex biological samples using TDP is still challenging due to high sample complexity and wide dynamic range. High-resolution separation methods are often applied prior to mass spectrometry (MS) analysis to decrease sample complexity and increase proteomics throughput. These separation methods, however, may not be efficient enough to characterize low abundance intact proteins in complex samples. As such, multidimensional separation techniques (combination of two or more separation methods with high orthogonality) have been developed and applied that demonstrate improved separation resolution and more comprehensive identification in TDP. A suite of multidimensional separation methods that couple various types of liquid chromatography (LC), capillary electrophoresis (CE), and/or gel electrophoresis-based separation approaches have been developed and applied in TDP to analyze complex biological samples. Here, we reviewed multidimensional separation strategies employed for TDP, summarized current applications, and discussed the gaps that may be addressed in the future.
Keywords: CE; LC; Top-down proteomics; gel electrophoresis; multidimensional separation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
