Prognostic utility of Fibrosis-4 Index for risk of subsequent liver and cardiovascular events, and all-cause mortality in individuals with obesity and/or type 2 diabetes: a longitudinal cohort study
- PMID: 38188279
- PMCID: PMC10769893
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2023.100780
Prognostic utility of Fibrosis-4 Index for risk of subsequent liver and cardiovascular events, and all-cause mortality in individuals with obesity and/or type 2 diabetes: a longitudinal cohort study
Abstract
Background: The Fibrosis-4 Index (FIB-4) is used as a non-invasive tool for the presence of advanced liver fibrosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and type 2 diabetes. However, evidence for an association between FIB-4 and risk of mortality and/or liver-related clinical outcomes is limited. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between FIB-4 and subsequent liver events, cardiovascular events, and all-cause mortality in individuals with obesity and/or type 2 diabetes examined in routine general practice.
Methods: This was a longitudinal cohort study in which eligible adults had obesity and/or type 2 diabetes and ≥1 FIB-4 score calculable from UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink GOLD after 1 January 2001. No alcohol-related disorders and/or chronic liver diseases (except non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) and/or no prescriptions of drugs inducing liver disease were permitted. Individuals were followed until time of first event, 10 years, or 1 January 2020. Analyses were conducted using Aalen-Johansen cumulative incidence functions and Cox proportional hazards models.
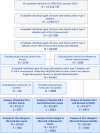
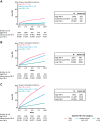
Findings: Among 44,481 included individuals (mean age 58·8 years; 54% female), there were 979 liver, 6002 cardiovascular, and 8971 mortality events during the 10 years of follow-up. At 10 years, the cumulative incidence of liver events in the high (>2·67), indeterminate (1·30-2·67), and low (<1·30) baseline FIB-4 risk groups were 15%, 3%, and 1%, respectively. Age- and sex-adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) for liver events were elevated in high (16·46; 95% confidence interval [CI] 13·65-19·85) and indeterminate (2·45; 95% CI 2·07-2·90) versus low FIB-4 risk groups. Similar results were found for cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality. Among 20,433 individuals with ≥2 FIB-4 measurements, increase/decrease in FIB-4 12 months after baseline was directly associated with risk of liver events: compared with individuals with low baseline FIB-4 and no change in FIB-4 (reference), the adjusted HR (95% CI) for those with high baseline FIB-4 was 24·27 (16·98-34·68) with a one-unit FIB-4 increase, and 10·90 (7·90-15·05) with a one-unit decrease.
Interpretation: In addition to its value as a diagnostic tool, FIB-4 has clinical utility as a prognostic biomarker. Sequential measurement provides a pragmatic, tractable monitoring biomarker that refines risk assessment for liver events, cardiovascular events, and mortality.
Funding: Novo Nordisk A/S.
Keywords: Cardiovascular events; FIB-4; Hepatic decompensation; Liver events; Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
QMA is coordinator of the IMI2 Liver Investigation: Testing Marker Utility in Steatohepatitis (LITMUS) consortium, which is funded by the European Union Horizon 2020 programme and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA). This multi-stakeholder consortium includes industry partners. He reports research grant funding from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Intercept; consultancy on behalf of Newcastle University for Alimentiv, Akero, AstraZeneca, Axcella, 89Bio, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Galmed, Genfit, Genentech, Gilead, GSK, Hanmi, HistoIndex, Intercept, Inventiva, Ionis, IQVIA, Janssen, Madrigal, Medpace, Merck, NGMBio, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, PathAI, Pfizer, Prosciento, Poxel, Resolution Therapeutics, Roche, Ridgeline Therapeutics, RTI, Shionogi, and Terns; speaker fees/honoraria from Fishawack, Integritas Communications, Kenes, Novo Nordisk, Madrigal, Medscape, and Springer Healthcare; and royalties from Elsevier. MJ, MSK, TLB, LMN, JMT, KKM, and ABJ are full-time employees and shareholders of Novo Nordisk A/S. KK has acted as consultant, advisory board member, and speaker for Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, and Servier; and received EACME grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi-Aventis.
Figures


References
-
- Taylor R.S., Taylor R.J., Bayliss S., et al. Association between fibrosis stage and outcomes of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1611–1625.e12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

