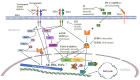
Endocrine therapy plus HER2-targeted therapy, another favorable option for HR+/HER2+ advanced breast cancer patients
- PMID: 38188468
- PMCID: PMC10771751
- DOI: 10.1177/17588359231220501
Endocrine therapy plus HER2-targeted therapy, another favorable option for HR+/HER2+ advanced breast cancer patients
Abstract
Advanced breast cancer (ABC) that is positive for hormone receptors (HRs) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is a cancer subtype with distinctive characteristics. The primary treatment guidelines suggest that a combination therapy comprising anti-HER2 therapy and chemotherapy should be administered as the initial treatment for HR-positive/ HER2-positive (HR+/HER2+) ABC. However, crosstalk between the HR and HER2 pathways can partially account for the resistance of HR+/HER2+ disease to HER2-targeted therapy. This, in turn, provides a rationale for the concomitant administration of HER2-targeted therapy and endocrine therapy (ET). Many clinical studies have confirmed that the combination of HER2-targeted therapy and ET as a first-line treatment is not inferior to the combination of HER2-targeted therapy and chemotherapy, and support its use as a first-line treatment choice for HR+/HER2+ ABC. Other drugs, such as antibody-drug conjugates, cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-protein kinase B (AKT)-mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors, and programmed cell death protein 1 or programmed cell death ligand 1 inhibitors, may also improve the prognosis of patients with breast cancer by blocking signaling pathways associated with tumor proliferation and break new ground for the treatment of HR+/HER2+ ABC.
Keywords: HER2+ breast cancer; antibody–drug conjugates; chemotherapy; combination therapy; endocrine therapy; hormone receptor-positive breast cancer; hormone therapy; targeted therapy.
© The Author(s), 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacoeconomic evaluations of CDK4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy for advanced hormone receptor-positive (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 negative (HER2-) breast cancer: a systematic review.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Feb;10(4):233. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-5110. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35280368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolving perspectives on the treatment of HR+/HER2+ metastatic breast cancer.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023 Aug 11;15:17588359231187201. doi: 10.1177/17588359231187201. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37576607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 negative advanced breast cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Feb;180(1):21-32. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05528-2. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 31970560 Review.
-
Molecularly targeted therapy and immunotherapy for hormone receptor‑positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2‑negative advanced breast cancer (Review).Oncol Rep. 2020 Jul;44(1):3-13. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7589. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32319666 Review.
-
Recent advances in the treatment of hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor 2-positive advanced breast cancer.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2021 May 6;13:17588359211013326. doi: 10.1177/17588359211013326. eCollection 2021. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33995599 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al.. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021; 71: 209–249. - PubMed
-
- Vici P, Pizzuti L, Natoli C, et al.. Triple positive breast cancer: a distinct subtype? Cancer Treat Rev 2015; 41: 69–76. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous