Kinetic modeling of leucine-mediated signaling and protein metabolism in human skeletal muscle
- PMID: 38188514
- PMCID: PMC10767222
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108634
Kinetic modeling of leucine-mediated signaling and protein metabolism in human skeletal muscle
Abstract
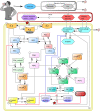
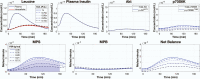
Skeletal muscle protein levels are governed by the relative rates of muscle protein synthesis (MPS) and breakdown (MPB). The mechanisms controlling these rates are complex, and their integrated behaviors are challenging to study through experiments alone. The purpose of this study was to develop and analyze a kinetic model of leucine-mediated mTOR signaling and protein metabolism in the skeletal muscle of young adults. Our model amalgamates published cellular-level models of the IRS1-PI3K-Akt-mTORC1 signaling system and of skeletal-muscle leucine kinetics with physiological-level models of leucine digestion and transport and insulin dynamics. The model satisfactorily predicts experimental data from diverse leucine feeding protocols. Model analysis revealed that total levels of p70S6K are a primary determinant of MPS, insulin signaling substantially affects muscle net protein balance via its effects on MPB, and p70S6K-mediated feedback of mTORC1 signaling reduces MPS in a dose-dependent manner.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Protein.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Excess leucine intake enhances muscle anabolic signaling but not net protein anabolism in young men and women.J Nutr. 2010 Nov;140(11):1970-6. doi: 10.3945/jn.110.127647. Epub 2010 Sep 15. J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20844186 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Whey Protein Hydrolysate Increases Amino Acid Uptake, mTORC1 Signaling, and Protein Synthesis in Skeletal Muscle of Healthy Young Men in a Randomized Crossover Trial.J Nutr. 2019 Jul 1;149(7):1149-1158. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxz053. J Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31095313 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dileucine ingestion is more effective than leucine in stimulating muscle protein turnover in young males: a double blind randomized controlled trial.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021 Sep 1;131(3):1111-1122. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00295.2021. Epub 2021 Jul 29. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021. PMID: 34323596 Clinical Trial.
-
A focus on leucine in the nutritional regulation of human skeletal muscle metabolism in ageing, exercise and unloading states.Clin Nutr. 2023 Oct;42(10):1849-1865. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2023.08.010. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Clin Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37625315 Review.
-
Dietary protein to support anabolism with resistance exercise in young men.J Am Coll Nutr. 2005 Apr;24(2):134S-139S. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2005.10719454. J Am Coll Nutr. 2005. PMID: 15798080 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Data on the Role of Amino Acids in the Management of Obesity in Children and Adolescents.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 24;26(15):7129. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157129. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Preliminary Study of Nutrients Related to the Risk of Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S) in Top-Performing Female Amateur Triathletes: Results from a Nutritional Assessment.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 7;17(2):208. doi: 10.3390/nu17020208. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39861337 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karagounis L.G., Hawley J.A. Skeletal muscle: increasing the size of the locomotor cell. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010;42:1376–1379. - PubMed
-
- Kraemer W.J., Ratamess N.A. Fundamentals of resistance training: progression and exercise prescription. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004;36:674–688. - PubMed
-
- Velázquez Alva M.d.C., Irigoyen Camacho M.E., Delgadillo Velázquez J., Lazarevich I. The relationship between sarcopenia,undernutrition, physical mobility and basic activities of daily living in a group of elderly women of Mexico City. Nutr. Hosp. 2013;28:514–521. - PubMed
-
- Cormie P., McGuigan M.R., Newton R.U. Developing maximal neuromuscular power: Part 1--biological basis of maximal power production. Sports Med. 2011;41:17–38. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

