Intracellular Ca2+ oscillation frequency and amplitude modulation mediate epithelial apical and basolateral membranes crosstalk
- PMID: 38188522
- PMCID: PMC10767210
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108629
Intracellular Ca2+ oscillation frequency and amplitude modulation mediate epithelial apical and basolateral membranes crosstalk
Abstract
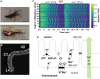
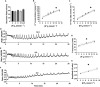
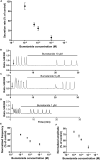
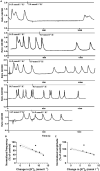
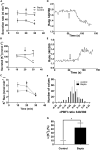
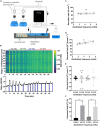
Since the early seminal studies on epithelial solute transport, it has been understood that there must be crosstalk among different members of the transport machinery to coordinate their activity and, thus, generate localized electrochemical gradients that force solute flow in the required direction that would otherwise be thermodynamically unfavorable. However, mechanisms underlying intracellular crosstalk remain unclear. We present evidence that crosstalk between apical and basolateral membrane transporters is mediated by intracellular Ca2+ signaling in insect renal epithelia. Ion flux across the basolateral membrane is encoded in the intracellular Ca2+ oscillation frequency and amplitude modulation and that information is used by the apical membrane to adjust ion flux accordingly. Moreover, imposing experimentally generated intracellular Ca2+ oscillation modulation causes cells to predictably adjust their ion transport properties. Our results suggest that intracellular Ca2+ oscillation frequency and amplitude modulation encode information on transmembrane ion flux that is required for crosstalk.
Keywords: Cell biology; Molecular physiology; Physiology.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stimulation of Cl- secretion via membrane-restricted Ca2+ signaling mediated by P2Y receptors in polarized epithelia.J Biol Chem. 2002 Mar 15;277(11):9016-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111917200. Epub 2002 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11779875
-
Apical versus basolateral P2Y(6) receptor-mediated Cl(-) secretion in immortalized bronchial epithelia.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009 Jun;40(6):733-45. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0020OC. Epub 2008 Nov 14. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19011163
-
Cortisol stimulates calcium transport across cultured gill epithelia from freshwater rainbow trout.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2008 Mar-Apr;44(3-4):96-104. doi: 10.1007/s11626-007-9077-6. Epub 2008 Feb 1. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2008. PMID: 18239979
-
Basolateral membrane K+ channels in renal epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 May 1;302(9):F1069-81. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00646.2011. Epub 2012 Feb 15. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22338089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrinsic regulation of apical sodium entry in epithelia.Physiol Rev. 1991 Apr;71(2):429-45. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.2.429. Physiol Rev. 1991. PMID: 1706528 Review.
References
-
- Schultz S.G. Homocellular regulatory mechanisms in sodium-transporting epithelia: avoidance of extinction by “flush-through.”. Am. J. Physiol. 1981;241:F579–F590. - PubMed
-
- Diamond J.M. Transcellular cross-talk between epithelial cell membranes. Nature. 1982;300:683–685. - PubMed
-
- Schultz S.G., Lapointe J.-Y. In: The Kidney: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Third Edition. Seldin D., Giebisch G., editors. Lippincott-Raven; 1999. Membrane cross-talk in sodium-absorbing epithelial cells.
-
- Krogh A. The active absorption of ions in some freshwater animals. Z Vergl. Physiol. 1938;25:335–350.
-
- Foskett J.K., Bern H.A., Machen T.E., Conner M. Chloride cells and the hormonal control of teleost fish osmoregulation. J. Exp. Biol. 1983;106:255–281. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

