[Liuwei Dihuang Pills alleviates postmenopausal osteoporosis and fatigue in rats by inhibiting the epigenetic regulatory molecule BRD4 pathway]
- PMID: 38189384
- PMCID: PMC10774109
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.12.02
[Liuwei Dihuang Pills alleviates postmenopausal osteoporosis and fatigue in rats by inhibiting the epigenetic regulatory molecule BRD4 pathway]
Abstract
Objective: To explore the role of epigenetic signal molecule bromodomain protein 4 (BRD4) in mediating the therapeutic effect of Liuwei Dihuang (LWDH) Pills on postmenopausal osteoporosis (PMOP) and fatigue.
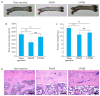
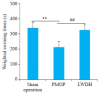
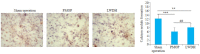
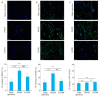
Methods: Thirty rat models of PMOP induced by bilateral ovariectomy were randomized equally into two groups for treatment with normal saline (model group) or LWDH Pills (385.7 mg/kg), with another 15 sham-operated rats as the sham operation group. After 12 weeks of treatment, femoral samples were taken to determine the bone density and BRD4 protein expression. The weight-bearing exhaustive swimming time of the rat models was recorded, and serum levels of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In cultured primary osteoblasts the changes in the expressions of BRD4, MAPK and NF-κB proteins were detected by immunofluorescence staining following treatment with LWDH Pills.
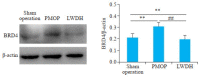
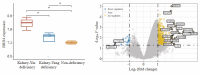
Results: The rat models of PMOP showed significantly up-regulated expression of BRD4 protein in the femoral tissue (P < 0.05), which was obviously lowered by treatment with LWDH Pills. The rats treated with LWDH Pills also showed significant improvement of fatigue. Immunofluorescent staining of the osteoblasts showed that treatment with LWDH Pills significantly decreased the protein expressions of BRD4, MAPK and NF-κB. Analysis of the GSE56116 dataset revealed that that patients with kidney-yin deficiency had significantly higher BRD4 expression than those in the kidney-yang-deficiency group and non-kidney-deficiency group (P < 0.05). The upregulation of BRD4 expression involved multiple signaling pathways including neural ligand receptor response, cytoskeleton rearrangement, cytokine interaction, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor chemotaxis pathways.
Conclusion: LWDH can alleviate PMOP and fatigue by decreasing BRD4 signaling pathway, suggesting that potential of BRD4 as a promising therapeutic target for PMOP.
目的: 基于表观遗传信号分子-溴结构域蛋白4(BRD4)表达探讨六味地黄丸治疗绝经后骨质疏松症(PMOP)及疲劳疗效的可能作用机制。
方法: 通过双侧卵巢摘除法制备PMOP大鼠模型;将大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组(生理盐水,10 mL/kg)、中药组(六味地黄丸385.7 mg/kg),15只/组。中药组治疗12周后取股骨标本检测股骨密度强度以及骨组织BRD4蛋白的表达。检测各组鼠模型负重力竭游泳时间;酶联免疫吸附法测定鼠血清环磷酸腺苷(cAMP),环磷酸鸟苷(cGMP)。原代培养成骨细胞,免疫荧光染色方法检测BRD4,MAPK和NF-κB蛋白的表达。
结果: Western blot检测结果发现,与假手术组相比较,模型组BRD4蛋白表达水平上调(P < 0.05);与模型大鼠相比较,中药组BRD4蛋白表达水平下调;鼠负重力竭游泳实验发现,中药组明显改善疲劳(P < 0.05)。成骨细胞免疫荧光染色方法检测显示,中药组BRD4,MAPK和NF-κB蛋白表达减少。GSE56116数据集分析发现,肾阴虚组BRD4表达明显高于肾阳虚组和非肾虚组(P < 0.05)。BRD4表达上调涉及神经配体受体反应、细胞骨架重排及细胞因子相互作用、粒细胞集落刺激因子趋化性等信号通路。
结论: 六味地黄丸可以减轻PMOP及疲劳表现,可能与BRD4表达减少以及BRD4介导的信号通路有关;BRD4有望成为PMOP潜在治疗靶点。
Keywords: Liuwei Dihuang Pills; bromodomain protein 4; fatigue; postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Network pharmacology-based strategy to investigate pharmacological mechanism of Liuwei Dihuang Pill against postmenopausal osteoporosis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Nov 25;101(47):e31387. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031387. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36451445 Free PMC article.
-
Liuwei Dihuang Pills alleviate the polycystic ovary syndrome with improved insulin sensitivity through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Mar 25;250:111965. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111965. Epub 2019 Jun 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31185267
-
Liuwei Dihuang pills attenuate ovariectomy-induced bone loss by alleviating bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC) senescence via the Yes-associated protein (YAP)-autophagy axis.Pharm Biol. 2024 Dec;62(1):42-52. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2023.2291675. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Pharm Biol. 2024. PMID: 38112463 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of Liuwei Dihuang on canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in osteoporosis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Apr 11;153(1):133-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.01.040. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24530448
-
Liuwei Dihuang Pill () Treats Postmenopausal Osteoporosis with Shen (Kidney) Yin Deficiency via Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription Signal Pathway by Up-regulating Cardiotrophin-Like Cytokine Factor 1 Expression.Chin J Integr Med. 2018 Jun;24(6):415-422. doi: 10.1007/s11655-016-2744-2. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Chin J Integr Med. 2018. PMID: 28028720 Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
