AAV-Mediated Gene Therapy Restores Hearing in Patients with DFNB9 Deafness
- PMID: 38189623
- PMCID: PMC10953563
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202306788
AAV-Mediated Gene Therapy Restores Hearing in Patients with DFNB9 Deafness
Erratum in
-
Correction to "AAV-Mediated Gene Therapy Restores Hearing in Patients with DFNB9 Deafness".Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 May;12(20):e2504047. doi: 10.1002/advs.202504047. Epub 2025 Apr 30. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40304279 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
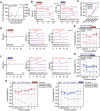
Mutations in OTOFERLIN (OTOF) lead to the autosomal recessive deafness 9 (DFNB9). The efficacy of adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated OTOF gene replacement therapy is extensively validated in Otof-deficient mice. However, the clinical safety and efficacy of AAV-OTOF is not reported. Here, AAV-OTOF is generated using good manufacturing practice and validated its efficacy and safety in mouse and non-human primates in order to determine the optimal injection dose, volume, and administration route for clinical trials. Subsequently, AAV-OTOF is delivered into one cochlea of a 5-year-old deaf patient and into the bilateral cochleae of an 8-year-old deaf patient with OTOF mutations. Obvious hearing improvement is detected by the auditory brainstem response (ABR) and the pure-tone audiometry (PTA) in these two patients. Hearing in the injected ear of the 5-year-old patient can be restored to the normal range at 1 month after AAV-OTOF injection, while the 8-year-old patient can hear the conversational sounds. Most importantly, the 5-year-old patient can hear and recognize speech only through the AAV-OTOF-injected ear. This study is the first to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of AAV-OTOF in patients, expands and optimizes current OTOF-related gene therapy and provides valuable information for further application of gene therapies for deafness.
Keywords: AAV; OTOF gene therapy; biosafety; clinical trial; hearing recovery.
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Z.Z., W.D., L.J., C.Y., J.L., L.W., and C.T. are paid employees of Otovia Therapeutics Inc. S.S. and H.S. are paid employees of Otovia Therapeutics Inc. and Fosun Health Capital. Other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Zhang Q. J., Han B., Lan L., Zong L., Shi W., Wang H. Y., Xie L. Y., Wang H., Zhao C., Zhang C., Yin Z. F., Wang D. Y., Petit C., Guan J., Wang Q. J., Clin. Genet. 2016, 90, 238. - PubMed
-
- Roux I., Safieddine S., Nouvian R., Grati M., Simmler M.‐C., Bahloul A., Perfettini I., Le Gall M., Rostaing P., Hamard G., Triller A., Avan P., Moser T., Petit C., Cell 2006, 127, 277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2021YFA1101300/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2021YFA1101800/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2020YFA0113600/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2020YFA0112503/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022ZD0205400/STI2030-Major Projects
- 82330033/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82030029/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 92149304/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82000984/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82371162/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82371161/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82071059/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BX20200082/China National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents
- 2020M681468/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 2021YFS0371/Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province
- YKY-KF202201/2022 Open Project Fund of Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences
- 2021K156B/Jiangsu Postdoctoral Research Funding Program
- YKK19072/Nanjing Medical Science and Technology Development Project
- JCYJ20190814093401920/Shenzhen Science and Technology Program
- JCYJ20210324125608022/Shenzhen Science and Technology Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
