Simulation-based establishment of base pools for a hybrid breeding program in winter rapeseed
- PMID: 38189816
- PMCID: PMC10774156
- DOI: 10.1007/s00122-023-04519-3
Simulation-based establishment of base pools for a hybrid breeding program in winter rapeseed
Abstract
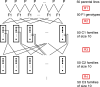
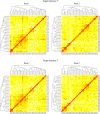
Simulation planned pre-breeding can increase the efficiency of starting a hybrid breeding program. Starting a hybrid breeding program commonly comprises a grouping of the initial germplasm in two pools and subsequent selection on general combining ability. Investigations on pre-breeding steps before starting the selection on general combining ability are not available. Our goals were (1) to use computer simulations on the basis of DNA markers and testcross data to plan crosses that separate genetically two initial germplasm pools of rapeseed, (2) to carry out the planned crosses, and (3) to verify experimentally the pool separation as well as the increase in testcross performance. We designed a crossing program consisting of four cycles of recombination. In each cycle, the experimentally generated material was used to plan the subsequent crossing cycle with computer simulations. After finishing the crossing program, the initially overlapping pools were clearly separated in principal coordinate plots. Doubled haploid lines derived from the material of crossing cycles 1 and 2 showed an increase in relative testcross performance for yield of about 5% per cycle. We conclude that simulation-designed pre-breeding crossing schemes, that were carried out before the general combining ability-based selection of a newly started hybrid breeding program, can save time and resources, and in addition conserve more of the initial genetic variation than a direct start of a hybrid breeding program with general combining ability-based selection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors AA, CF, KB, and TK are employed by Norddeutsche Pflanzenzucht Hans-Georg Lembke, Hohenlieth Hof, Holtsee, Germany. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Barata C, Carena MJ. Classification of North Dakota maize inbred lines into heterotic groups based on molecular and testcross data. Euphytica. 2006;151:339–349. doi: 10.1007/s10681-006-9155-y. - DOI
-
- Bidhendi MZ, Choukan R, Darvish F, Mostafavi K, Majidi E, Plant A. Classifying of maize inbred lines into heterotic groups using diallel analysis Mozhgan. Int J Biol Biomol Agric Food Biotechnol Eng. 2012;6:556–559.
-
- Butruille DV, Silva HD, Kaeppler SM, Coors JG. Response to selection and genetic drift in three populations derived from the golden glow maize population. Crop Sci. 2004;44:1527–1534. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2004.1527. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

