The human Y and inactive X chromosomes similarly modulate autosomal gene expression
- PMID: 38190107
- PMCID: PMC10794785
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100462
The human Y and inactive X chromosomes similarly modulate autosomal gene expression
Abstract
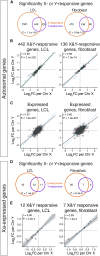
Somatic cells of human males and females have 45 chromosomes in common, including the "active" X chromosome. In males the 46th chromosome is a Y; in females it is an "inactive" X (Xi). Through linear modeling of autosomal gene expression in cells from individuals with zero to three Xi and zero to four Y chromosomes, we found that Xi and Y impact autosomal expression broadly and with remarkably similar effects. Studying sex chromosome structural anomalies, promoters of Xi- and Y-responsive genes, and CRISPR inhibition, we traced part of this shared effect to homologous transcription factors-ZFX and ZFY-encoded by Chr X and Y. This demonstrates sex-shared mechanisms by which Xi and Y modulate autosomal expression. Combined with earlier analyses of sex-linked gene expression, our studies show that 21% of all genes expressed in lymphoblastoid cells or fibroblasts change expression significantly in response to Xi or Y chromosomes.
Keywords: CRISPR; Klinefelter syndrome; Turner syndrome; X chromosome inactivation; aneuploidy; gene expression; sex chromosomes; sex differences; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
The human Y and inactive X chromosomes similarly modulate autosomal gene expression.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 7:2023.06.05.543763. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.05.543763. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cell Genom. 2024 Jan 10;4(1):100462. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100462. PMID: 37333288 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Ohno S. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 1967. Sex Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Genes.
-
- Lahn B.T., Page D.C. Four evolutionary strata on the human X chromosome. Science. 1999;286:964–967. - PubMed
-
- Lyon M.F. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.) Nature. 1961;190:372–373. - PubMed
-
- Brown C.J., Ballabio A., Rupert J.L., Lafreniere R.G., Grompe M., Tonlorenzi R., Willard H.F. A gene from the region of the human X inactivation centre is expressed exclusively from the inactive X chromosome. Nature. 1991;349:38–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

