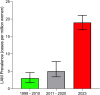
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: No Longer Ultra-rare
- PMID: 38190704
- PMCID: PMC10878381
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202312-2254ED
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: No Longer Ultra-rare
Figures
Comment on
-
Updated Prevalence of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Europe.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Feb 15;209(4):456-459. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202310-1736LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38060201 No abstract available.
References
-
- McCarthy C, Gupta N, Johnson SR, Yu JJ, McCormack FX. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis, and management. Lancet Respir Med . 2021;9:1313–1327. - PubMed
-
- Ryu JH, Sykes AM, Lee AS, Burger CD. Cystic lung disease is not uncommon in men with tuberous sclerosis complex. Respir Med . 2012;106:1586–1590. - PubMed
-
- Urban T, Lazor R, Lacronique J, Murris M, Labrune S, Valeyre D, et al. Pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis: a study of 69 patients. Groupe d’Etudes et de Recherche sur les Maladies “Orphelines” Pulmonaires (GERM“O”P) Medicine (Baltimore) . 1999;78:321–337. - PubMed
-
- Hayashida M, Seyama K, Inoue Y, Fujimoto K, Kubo K, Respiratory Failure Research Group of the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare The epidemiology of lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Japan: a nationwide cross-sectional study of presenting features and prognostic factors. Respirology . 2007;12:523–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical