Distinct mesenchymal cell states mediate prostate cancer progression
- PMID: 38191471
- PMCID: PMC10774315
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44210-1
Distinct mesenchymal cell states mediate prostate cancer progression
Abstract
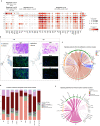
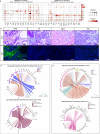
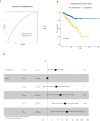
In the complex tumor microenvironment (TME), mesenchymal cells are key players, yet their specific roles in prostate cancer (PCa) progression remain to be fully deciphered. This study employs single-cell RNA sequencing to delineate molecular changes in tumor stroma that influence PCa progression and metastasis. Analyzing mesenchymal cells from four genetically engineered mouse models (GEMMs) and correlating these findings with human tumors, we identify eight stromal cell populations with distinct transcriptional identities consistent across both species. Notably, stromal signatures in advanced mouse disease reflect those in human bone metastases, highlighting periostin's role in invasion and differentiation. From these insights, we derive a gene signature that predicts metastatic progression in localized disease beyond traditional Gleason scores. Our results illuminate the critical influence of stromal dynamics on PCa progression, suggesting new prognostic tools and therapeutic targets.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Update of
-
Distinct mesenchymal cell states mediate prostate cancer progression.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 1:2023.03.29.534769. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.29.534769. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 8;15(1):363. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44210-1. PMID: 37034687 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

