Deciphering the role of neddylation in tumor microenvironment modulation: common outcome of multiple signaling pathways
- PMID: 38191508
- PMCID: PMC10773064
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-023-00545-x
Deciphering the role of neddylation in tumor microenvironment modulation: common outcome of multiple signaling pathways
Abstract
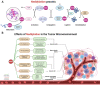
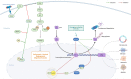
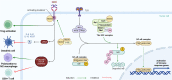
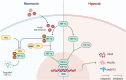
Neddylation is a post-translational modification process, similar to ubiquitination, that controls several biological processes. Notably, it is often aberrantly activated in neoplasms and plays a critical role in the intricate dynamics of the tumor microenvironment (TME). This regulatory influence of neddylation permeates extensively and profoundly within the TME, affecting the behavior of tumor cells, immune cells, angiogenesis, and the extracellular matrix. Usually, neddylation promotes tumor progression towards increased malignancy. In this review, we highlight the latest understanding of the intricate molecular mechanisms that target neddylation to modulate the TME by affecting various signaling pathways. There is emerging evidence that the targeted disruption of the neddylation modification process, specifically the inhibition of cullin-RING ligases (CRLs) functionality, presents a promising avenue for targeted therapy. MLN4924, a small-molecule inhibitor of the neddylation pathway, precisely targets the neural precursor cell-expressed developmentally downregulated protein 8 activating enzyme (NAE). In recent years, significant advancements have been made in the field of neddylation modification therapy, particularly the integration of MLN4924 with chemotherapy or targeted therapy. This combined approach has demonstrated notable success in the treatment of a variety of hematological and solid tumors. Here, we investigated the inhibitory effects of MLN4924 on neddylation and summarized the current therapeutic outcomes of MLN4924 against various tumors. In conclusion, this review provides a comprehensive, up-to-date, and thorough overview of neddylation modifications, and offers insight into the critical importance of this cellular process in tumorigenesis.
Keywords: Clinical trials; MLN4924; NEDD8; Neddylation; Signaling pathway; TME.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting Neddylation pathways to inactivate cullin-RING ligases for anticancer therapy.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Dec 10;21(17):2383-400. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5795. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24410571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of tumor angiogenesis by targeting the protein neddylation pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Feb 13;5(2):e1059. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.21. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24525735 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting protein neddylation with an NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 induced apoptosis or senescence in human lymphoma cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(3):420-9. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2014.1003003. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25782162 Free PMC article.
-
Neddylation-Independent Activities of MLN4924.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1217:363-372. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1025-0_21. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31898238 Review.
-
The Double-Edged Effects of MLN4924: Rethinking Anti-Cancer Drugs Targeting the Neddylation Pathway.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 21;14(7):738. doi: 10.3390/biom14070738. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062453 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of neddylation on prognosis in the immune microenvironment of neuroblastoma: a single-cell transcriptomic analysis.Immunol Res. 2025 Jul 17;73(1):107. doi: 10.1007/s12026-025-09662-1. Immunol Res. 2025. PMID: 40676385
-
Pan-cancer analysis unveils the role and mechanisms of neddylation modifications in tumorigenesis.Med Oncol. 2025 Mar 19;42(4):119. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02658-9. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40106140
-
Protein neddylation and its role in health and diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Apr 5;9(1):85. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01800-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38575611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-omics Analysis Revealed the Diagnostic and Therapeutic Value of Immunogenic Cell Death-derived SCN5A in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 24. doi: 10.1007/s12033-025-01444-2. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40272736
-
Transcriptomic profiling of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: dysregulation of WNT, MAPK, PI3K, neddylation pathways and potential non-invasive biomarkers.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 16;20(6):e0325672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325672. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40522948 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

