Seroprevalence of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Remained Extremely Low in Taiwan Until the Vaccination Program Was Implemented
- PMID: 38192381
- PMCID: PMC10773475
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofad614
Seroprevalence of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Remained Extremely Low in Taiwan Until the Vaccination Program Was Implemented
Abstract
Background: The Taiwanese government made a concerted effort to contain a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) nosocomial outbreak of variant B.1.429, shortly before universal vaccination program implementation. This study aimed to investigate seroprevalence in the highest-risk regions.
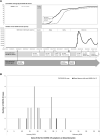
Methods: Between January and February 2021, we retrieved 10 000 repository serum samples from blood donors to examine for antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) nucleocapsid (N) and spike (S) antigens. A positive result was confirmed if anti-N and anti-S antibodies were positive. Overall, 2000 donors residing in the highest-risk district and donating blood in January 2021 were further examined for SARS-CoV-2 RNA. We estimated seroprevalence and compared the epidemic curve between confirmed COVID-19 cases and blood donors with positive antibodies or viral RNA.
Results: Twenty-one cases with COVID-19 were confirmed in the nosocomial cluster, with an incidence of 1.27/100 000 in the COVID-affected districts. Among 4888 close contacts of the nosocomial cases, 20 (0.4%) became confirmed cases during isolation. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 was detected in 2 of the 10000 blood donors, showing a seroprevalence of 2/10000 (95% CI, 0.55-7.29). None of the 2000 donors who underwent tests for SARS-CoV-2 RNA were positive. The SARS-CoV-2 infection epidemic curve was observed sporadically in blood donors compared with the nosocomial cluster.
Conclusions: In early 2021, an extremely low anti-SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence among blood donors was observed. Epidemic control measures through precise close contact tracing, testing, and isolation effectively contained SARS-CoV-2 transmission before universal vaccination program implementation.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; nosocomial infection; seroprevalence; transfusion safety.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: no reported conflicts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changing Patterns of SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence among Canadian Blood Donors during the Vaccine Era.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0033922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00339-22. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35412385 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence estimates between commercial lab serum specimens and blood donor specimens, United States, September-December 2021.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Aug 6;12(8):e0012324. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00123-24. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38869287 Free PMC article.
-
Serosurveillance of SARS-CoV-2 in Welsh Blood Donors: Establishment of the surveillance system and results up to November 2022.Euro Surveill. 2023 May;28(19):2200473. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2023.28.19.2200473. Euro Surveill. 2023. PMID: 37166761 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence of anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 antibody among healthy blood donors in a hospital-based blood center in Eastern India during the COVID-19 pandemic.Asian J Transfus Sci. 2022 Jan-Jun;16(1):15-21. doi: 10.4103/ajts.ajts_123_20. Epub 2022 May 26. Asian J Transfus Sci. 2022. PMID: 36199419 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies among blood donors in Québec: an update from a serial cross-sectional study.Can J Public Health. 2022 Jun;113(3):385-393. doi: 10.17269/s41997-022-00622-y. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Can J Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35380364 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Door-to-Device Time Segments and Clinical Outcomes for STEMI Patients in Northern Taiwan.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2025 Jan;41(1):121-129. doi: 10.6515/ACS.202501_41(1).20241021A. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39776930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hick JL, Biddinger PD. Novel coronavirus and old lessons-preparing the health system for the pandemic. N Engl J Med 2020; 382:e55. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

