Anonymizing at-home fitness: enhancing privacy and motivation with virtual reality and try-on
- PMID: 38192556
- PMCID: PMC10773911
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1333776
Anonymizing at-home fitness: enhancing privacy and motivation with virtual reality and try-on
Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to address privacy concerns associated with video conferencing tools used in home-based exercise training. To that end, a method that could anonymize participants' appearances and exercise environments during at-home fitness sessions was proposed.
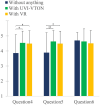
Methods: This method combines virtual reality for 3-D human-model rendering using key-points tracking with a virtual try-on system enhanced by UV mapping and instance segmentation. To validate the proposed method, we conducted a user study by recruiting participants to assess effectiveness of virtual reality and virtual try-on in terms of privacy protection, self-confidence, and coaching satisfaction.
Results: Experimental results demonstrated the effectiveness and improved user experience of using virtual reality or virtual try-on in remote fitness, particularly in enhancing privacy protection and self-confidence with statistical significance. However, no significant differences were noted in coaching satisfaction.
Discussion: These findings confirmed the efficacy of our proposed approach. We believe that the proposed approach can significantly contribute to the future of remote fitness training, offering a more secure and engaging environment for users, thereby potentially increasing adherence to fitness regimens and overall physical wellbeing.
Keywords: fitness apps; physical activity; physical health; smart applications; virtual reality exercise; virtual try-on.
Copyright © 2023 Yoon, Jeong, Kim and Lim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Ráthonyi G, Kósa K, Bács Z, Ráthonyi-Ódor K, Füzesi I, Lengyel P, et al. Changes in workers' physical activity and sedentary behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sustainability. (2021) 13:9524. 10.3390/su13179524 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

