Immunoinformatics-aided rational design of a multi-epitope vaccine targeting feline infectious peritonitis virus
- PMID: 38192725
- PMCID: PMC10773687
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1280273
Immunoinformatics-aided rational design of a multi-epitope vaccine targeting feline infectious peritonitis virus
Abstract
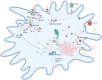
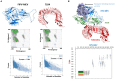
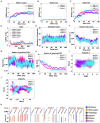
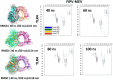
Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) is a grave and frequently lethal ailment instigated by feline coronavirus (FCoV) in wild and domestic feline species. The spike (S) protein of FCoV assumes a critical function in viral ingress and infection, thereby presenting a promising avenue for the development of a vaccine. In this investigation, an immunoinformatics approach was employed to ascertain immunogenic epitopes within the S-protein of FIP and formulate an innovative vaccine candidate. By subjecting the amino acid sequence of the FIP S-protein to computational scrutiny, MHC-I binding T-cell epitopes were predicted, which were subsequently evaluated for their antigenicity, toxicity, and allergenicity through in silico tools. Our analyses yielded the identification of 11 potential epitopes capable of provoking a robust immune response against FIPV. Additionally, molecular docking analysis demonstrated the ability of these epitopes to bind with feline MHC class I molecules. Through the utilization of suitable linkers, these epitopes, along with adjuvants, were integrated to design a multi-epitope vaccine candidate. Furthermore, the stability of the interaction between the vaccine candidate and feline Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) was established via molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation analyses. This suggests good prospects for future experimental validation to ascertain the efficacy of our vaccine candidate in inducing a protective immune response against FIP.
Keywords: feline coronavirus; feline infectious peritonitis; immunoinformatics; reverse vaccinology; spike protein; vaccine.
Copyright © 2023 Chawla, Cuspoca, Akthar, Magdaleno, Rattanabunyong, Suwattanasophon, Jongkon, Choowongkomon, Shaikh, Malik and Cavallo.
Conflict of interest statement
NA and AS were employed by the company STEMskills Research and Education Lab Private Limited, India. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immunoinformatics design of a novel epitope-based vaccine candidate against dengue virus.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 5;11(1):19707. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99227-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34611250 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of Full-Length cDNA Clones and an Efficient Oral Infection Model for Feline Coronavirus in Cats.J Virol. 2021 Oct 13;95(21):e0074521. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00745-21. Epub 2021 Aug 18. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34406859 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated multi-pronged reverse vaccinology and biophysical approaches for identification of potential vaccine candidates against Nipah virus.Saudi Pharm J. 2023 Dec;31(12):101826. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.101826. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Saudi Pharm J. 2023. PMID: 38028215 Free PMC article.
-
Feline Coronaviruses: Pathogenesis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis.Adv Virus Res. 2016;96:193-218. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2016.08.002. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Adv Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 27712624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational epitope-based vaccine design with bioinformatics approach; a review.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 4;11(1):e41714. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41714. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39866399 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of multi-epitope Cathepsin L driven short peptide vaccine against Fasciola gigantica.Front Vet Sci. 2025 May 22;12:1547937. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1547937. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40475029 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Design and Characterization of a Multiepitope Vaccine Candidate Against Brucella canis Using a Reverse Vaccinology Approach.J Immunol Res. 2025 Apr 15;2025:6348238. doi: 10.1155/jimr/6348238. eCollection 2025. J Immunol Res. 2025. PMID: 40265107 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating immunoinformatics and computational epitope prediction for a vaccine candidate against respiratory syncytial virus.Infect Dis Model. 2024 Apr 16;9(3):763-774. doi: 10.1016/j.idm.2024.04.005. eCollection 2024 Sep. Infect Dis Model. 2024. PMID: 38708060 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a candidate mRNA vaccine based on Multi-Peptide targeting VP4 of rotavirus A: an immunoinformatics and molecular dynamics approach.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22610. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07433-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594603 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-epitope Based Peptide Vaccine Candidate Against Babesia Infection From Rhoptry-Associated Protein 1 (RAP-1) Antigen Using Immuno-Informatics: An In Silico Approach.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2024 Dec 16;18:11779322241287114. doi: 10.1177/11779322241287114. eCollection 2024. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2024. PMID: 39691583 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

