Prognostic factors for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer with liver metastasis and establishment of novel nomograms for prediction: a SEER-based study
- PMID: 38193003
- PMCID: PMC10774045
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-23-874
Prognostic factors for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer with liver metastasis and establishment of novel nomograms for prediction: a SEER-based study
Abstract
Background: The prognosis of patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer with liver metastasis (BCLM) remains dismal and varies widely from person to person. Thus, we sought to construct nomograms to predict overall survival (OS) and breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS) in patients with HR-positive BCLM using data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) database.
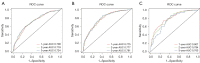
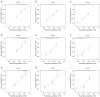
Methods: The data of patients with BCLM, who had received HR-positive diagnoses between 2010 and 2016, were collected from the SEER database. A Cox proportional hazards model was used to evaluate and identify the independent risk factors for OS and BCSS. Subsequently, two new nomograms were developed. Finally, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, calibration curves, and decision curve analysis (DCA) results were evaluated.
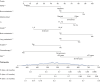
Results: The data of 1,780 patients diagnosed between 2010 and 2015 were used to build the nomogram models. Using both univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses, nine variables, including age, marital status, grade, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status, chemotherapy, surgery, bone metastasis, lung metastasis, and brain metastasis, were found to be significantly associated with OS. Conversely, 10 variables, including age, marital status, T stage, grade, HER2 status, chemotherapy, surgery, bone metastasis, lung metastasis, and brain metastasis, were identified as independent risk factors for BCSS. Using the risk factors listed above, we created 1-, 2-, and 3-year survival nomograms for OS and BCSS, respectively. Subsequently, the data of 312 patients, who had been diagnosed in 2016, were used for the external validation. These results, including the ROC curve, calibration curve, and DCA results, showed that our nomogram had strong predictive power.
Conclusions: Nomograms can effectively and reliably predict a patient's prognosis and could be useful in clinical decision making. The nomograms had strong discrimination, calibration, and clinical values. More aggressive treatment and closer monitoring should be considered when treating high-risk individuals.
Keywords: Breast cancer (BC); hormone receptor-positive (HR-positive); liver metastasis; nomogram; prognosis factors.
2023 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-23-874/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prognostic nomograms for breast cancer with lung metastasis: a SEER-based population study.BMC Womens Health. 2024 Jan 3;24(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02848-5. BMC Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 38172874 Free PMC article.
-
An effective tool for predicting survival in breast cancer patients with de novo lung metastasis: Nomograms constructed based on SEER.Front Surg. 2023 Jan 6;9:939132. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.939132. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 36684376 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a prognostic nomogram for lymph node positive HR+/HER2- breast cancer patients: a study of SEER database and a Chinese cohort.Gland Surg. 2023 Nov 24;12(11):1541-1553. doi: 10.21037/gs-23-177. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Gland Surg. 2023. PMID: 38107492 Free PMC article.
-
A New Online Dynamic Nomogram: Construction and Validation of a Predictive Model for Distant Metastasis Risk and Prognosis in Patients with Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors.J Gastrointest Surg. 2023 Jul;27(7):1429-1444. doi: 10.1007/s11605-023-05706-9. Epub 2023 May 25. J Gastrointest Surg. 2023. PMID: 37231240 Review.
-
Analysis of prognostic factors of metastatic endometrial cancer based on surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database.Front Surg. 2023 Jan 6;9:1001791. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1001791. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 36684133 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nomogram for predicting survival in breast cancer with lung metastasis based on SEER data.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Feb 28;14(2):808-826. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1047. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40104706 Free PMC article.
-
Survival outcomes, multidimensional prediction and subsequent therapy in patients with hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer receiving palbociclib: a real-world analysis.Gland Surg. 2024 Dec 31;13(12):2313-2324. doi: 10.21037/gs-24-362. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Gland Surg. 2024. PMID: 39822368 Free PMC article.
-
Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart.Open Med (Wars). 2025 Mar 21;20(1):20241103. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-1103. eCollection 2025. Open Med (Wars). 2025. PMID: 40129529 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
