The implication of targeting PD-1:PD-L1 pathway in treating sepsis through immunostimulatory and anti-inflammatory pathways
- PMID: 38193090
- PMCID: PMC10773890
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1323797
The implication of targeting PD-1:PD-L1 pathway in treating sepsis through immunostimulatory and anti-inflammatory pathways
Abstract
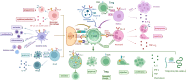
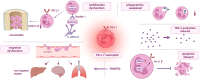
Sepsis currently remains a major contributor to mortality in the intensive care unit (ICU), with 48.9 million cases reported globally and a mortality rate of 22.5% in 2017, accounting for almost 20% of all-cause mortality worldwide. This highlights the urgent need to improve the understanding and treatment of this condition. Sepsis is now recognized as a dysregulation of the host immune response to infection, characterized by an excessive inflammatory response and immune paralysis. This dysregulation leads to secondary infections, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), and ultimately death. PD-L1, a co-inhibitory molecule expressed in immune cells, has emerged as a critical factor in sepsis. Numerous studies have found a significant association between the expression of PD-1/PD-L1 and sepsis, with a particular focus on PD-L1 expressed on neutrophils recently. This review explores the role of PD-1/PD-L1 in immunostimulatory and anti-inflammatory pathways, illustrates the intricate link between PD-1/PD-L1 and sepsis, and summarizes current therapeutic approaches against PD-1/PD-L1 in the treatment and prognosis of sepsis in preclinical and clinical studies.
Keywords: PD-1/PD-L1; immune homeostasis; immunoparalysis; organ damage; sepsis; treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Guo, Zhu, Ren, Sun, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune Deregulation in Sepsis and Septic Shock: Reversing Immune Paralysis by Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 17;11:624279. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.624279. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the programmed cell death 1: programmed cell death ligand 1 pathway reverses T cell exhaustion in patients with sepsis.Crit Care. 2014 Jan 4;18(1):R3. doi: 10.1186/cc13176. Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 24387680 Free PMC article.
-
PD-1 signaling pathway in sepsis: Does it have a future?Clin Immunol. 2021 Aug;229:108742. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2021.108742. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33905818 Review.
-
Frontline Science: Defects in immune function in patients with sepsis are associated with PD-1 or PD-L1 expression and can be restored by antibodies targeting PD-1 or PD-L1.J Leukoc Biol. 2016 Dec;100(6):1239-1254. doi: 10.1189/jlb.4HI0616-255R. Epub 2016 Sep 26. J Leukoc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27671246 Free PMC article.
-
[Role and application of programmed death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1 in immune cell dysfunction in sepsis: An update].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Sep;36(9):843-848. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32967768 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the Intricate Causal Nexus Between 91 Circulating Inflammatory Proteins and Perianal Abscess Through a Comprehensive Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis.Health Sci Rep. 2025 May 29;8(6):e70803. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70803. eCollection 2025 Jun. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40453734 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate's impact on immune cells in sepsis: unraveling the complex interplay.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 20;15:1483400. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1483400. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39372401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of PD-1/PD-L1 and IL-7 in Lymphocyte Dynamics and Sepsis Progression: A Biomarker Study in Critically Ill Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 24;25(23):12612. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312612. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684323 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Different Nicotine Sources on Exercise-Driven Immune Responses of Peripheral Blood Monocytes.Toxics. 2025 Jun 2;13(6):472. doi: 10.3390/toxics13060472. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40559945 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of soluble programmed death-1 and soluble programmed death ligand-1 in severe traumatic brain injury patients.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 11;14(1):23791. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74520-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39394380 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

