Hydrophobic ion pairing and microfluidic nanoprecipitation enable efficient nanoformulation of a small molecule indolamine 2, 3-dioxygenase inhibitor immunotherapeutic
- PMID: 38193128
- PMCID: PMC10771570
- DOI: 10.1002/btm2.10599
Hydrophobic ion pairing and microfluidic nanoprecipitation enable efficient nanoformulation of a small molecule indolamine 2, 3-dioxygenase inhibitor immunotherapeutic
Abstract
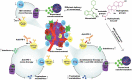
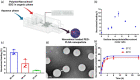
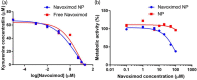
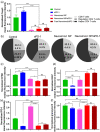
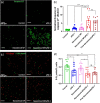
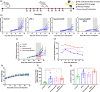
Blockade of programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) is a transformative immunotherapy. However, only a fraction of patients benefit, and there is a critical need for broad-spectrum checkpoint inhibition approaches that both enhance the recruitment of cytotoxic immune cells in cold tumors and target resistance pathways. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase (IDO) small molecule inhibitors are promising but suboptimal tumor bioavailability and dose-limiting toxicity have limited therapeutic benefits in clinical trials. This study reports on a nanoformulation of the IDO inhibitor navoximod within polymeric nanoparticles prepared using a high-throughput microfluidic mixing device. Hydrophobic ion pairing addresses the challenging physicochemical properties of navoximod, yielding remarkably high loading (>10%). The nanoformulation efficiently inhibits IDO and, in synergy with PD-1 antibodies improves the anti-cancer cytotoxicity of T-cells, in vitro and in vivo. This study provides new insight into the IDO and PD-1 inhibitors synergy and validates hydrophobic ion pairing as a simple and clinically scalable formulation approach.
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy; hydrophobic ion pairing; immune checkpoint inhibitors; indoleamine 2, 3‐dioxygenase; nanomedicine.
© 2023 The Authors. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycogen kinase 3 inhibitor nanoformulation as an alternative strategy to inhibit PD-1 immune checkpoint.Int J Pharm. 2022 Jun 25;622:121845. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121845. Epub 2022 May 22. Int J Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35613652
-
Modularly Designed Peptide Nanoprodrug Augments Antitumor Immunity of PD-L1 Checkpoint Blockade by Targeting Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Feb 5;142(5):2490-2496. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b12232. Epub 2020 Jan 24. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 31944687
-
Triple blockade of Ido-1, PD-L1 and MEK as a potential therapeutic strategy in NSCLC.J Transl Med. 2022 Nov 22;20(1):541. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03730-y. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36419183 Free PMC article.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (Ido) inhibitors and their nanomedicines for cancer immunotherapy.Biomaterials. 2021 Sep;276:121018. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121018. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Biomaterials. 2021. PMID: 34284200 Review.
-
Indoleamine Dioxygenase Inhibitors: Clinical Rationale and Current Development.Curr Oncol Rep. 2019 Jan 18;21(1):2. doi: 10.1007/s11912-019-0750-1. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30659394 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

