Emergency services utilization by patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis: An analysis of national trends
- PMID: 38193831
- PMCID: PMC10783841
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.15223
Emergency services utilization by patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis: An analysis of national trends
Abstract
Background: Hospitalization and mortality in patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis (AH), a severe form of liver disease, continue to increase over time. Given the severity of the illness, most hospitalized patients with AH are admitted from the emergency department (ED). However, there are no data on ED utilization by patients with AH. Thus, the Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS) dataset was analyzed to determine the ED utilization for AH.
Methods: Temporal trends (2016-2019) and outcomes of ED visits for AH were determined. Primary or secondary AH diagnoses were based on coding priority. Numbers of patients evaluated in the ED, severity of disease, complications of liver disease, and discharge disposition were analyzed. Crude and adjusted rates were examined, and temporal trends evaluated using logistic regression with orthogonal polynomial contrasts for each year.
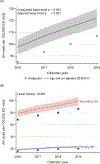
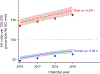
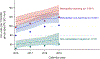
Results: There were 466,014,370 ED visits during 2016-2019, of which 448,984 (0.096%) were for AH, 85.0% of which required hospitalization. The rate of visits for AH (primary and secondary) between 2016 and 2019 increased from 85 to 106.8/100,000 ED visits. The rate of secondary AH increased more than the rate of primary AH (from 68.6 to 86.5 vs. from 16.4 to 20.3/100,000 ED visits). Patients aged 45-64 years had the highest rate of ED visits for AH, which decreased during the study period, while the rate of ED visits for AH increased in those aged 25-44 years (from 38.5% to 42.9%). The severity of disease (ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, and acute kidney injury) also increased over time. Medicaid and private insurance were the most common payors for patients seeking care in the ED for AH.
Conclusions: Temporal trends show an overall increase in ED utilization rates for AH, more patients requiring hospitalization, and an increase in the proportion of younger patients presenting to the ED with AH.
Keywords: Nationwide Emergency Department Sample; alcohol use disorder; alcohol-associated liver disease; emergency department; outcomes.
© 2023 Research Society on Alcohol.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: nothing to report
Figures

References
-
- Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project. Elixhauser Comorbidity Software Refined for ICD-10-CM, v2022.1.
-
- Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project. HCUP Methods Series.Introduction to the HCUP Nationwide Readmissions Databse (NRD) 2010–2018. . Available at: https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/nation/nrd/Introduction_NRD_2010-2018.jsp. Accessed.
-
- Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project. Requirements for Publishing Results with HCUP Data. .
-
- United States Census Bureau. Age and Sex Composition in the United States: 2010. Table 1. Population.
Grants and funding
- R56 HL141744/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062470/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061732/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062470-17S2/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL141744/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA028190/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA024333/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK060596/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AA028794/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK133905/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR 071046/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA024333/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061732/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA021890/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- RO1 DK113196/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA026976-03S1/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM119174/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR071046/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA 026976/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AA022742/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083414/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA021890/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA026976/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK130180/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AA028794/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK113196/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM119174/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HS026937/HS/AHRQ HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

