Normal Risk Ovarian Screening Study: 21-Year Update
- PMID: 38194613
- PMCID: PMC11003507
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.00141
Normal Risk Ovarian Screening Study: 21-Year Update
Abstract
Purpose: The Normal Risk Ovarian Screening Study (NROSS) tested a two-stage screening strategy in postmenopausal women at conventional hereditary risk where significantly rising cancer antigen (CA)-125 prompted transvaginal sonography (TVS) and abnormal TVS prompted surgery to detect ovarian cancer.
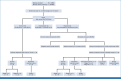
Methods: A total of 7,856 healthy postmenopausal women were screened annually for a total of 50,596 woman-years in a single-arm study (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00539162). Serum CA125 was analyzed with the Risk of Ovarian Cancer Algorithm (ROCA) each year. If risk was unchanged and <1:2,000, women returned in a year. If risk increased above 1:500, TVS was undertaken immediately, and if risk was intermediate, CA125 was repeated in 3 months with a further increase in risk above 1:500 prompting referral for TVS. An average of 2% of participants were referred to TVS annually.
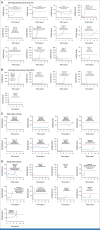
Results: Thirty-four patients were referred for operations detecting 15 ovarian cancers and two borderline tumors with 12 in early stage (I-II). In addition, seven endometrial cancers were detected with six in stage I. As four ovarian cancers and two borderline tumors were diagnosed with a normal ROCA, the sensitivity for detecting ovarian and borderline cancer was 74% (17 of 23), and 70% of ROCA-detected cases (12 of 17) were in stage I-II. NROSS screening reduced late-stage (III-IV) disease by 34% compared with UKCTOCS controls and by 30% compared with US SEER values. The positive predictive value (PPV) was 50% (17 of 34) for detecting ovarian cancer and 74% (25 of 34) for any cancer, far exceeding the minimum acceptable study end point of 10% PPV.
Conclusion: While the NROSS trial was not powered to detect reduced mortality, the high specificity, PPV, and marked stage shift support further development of this strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Surveillance Research Program (SRP) in NCI's Division of Cancer Control and Population Sciences (DCCPS) : Cancer Stat Facts: Ovarian Cancer. 2023. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/ovary.html
-
- Havrilesky LJ, Sanders GD, Kulasingam S, et al. : Development of an ovarian cancer screening decision model that incorporates disease heterogeneity: Implications for potential mortality reduction. Cancer 117:545-553, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Skates SJ, Menon U, MacDonald N, et al. : Calculation of the risk of ovarian cancer from serial CA-125 values for preclinical detection in postmenopausal women. J Clin Oncol 21:206s-210s, 2003. (10 suppl) - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

