Adjuvant Abemaciclib Plus Endocrine Therapy for Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative, High-Risk Early Breast Cancer: Results From a Preplanned monarchE Overall Survival Interim Analysis, Including 5-Year Efficacy Outcomes
- PMID: 38194616
- PMCID: PMC10950161
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.01994
Adjuvant Abemaciclib Plus Endocrine Therapy for Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative, High-Risk Early Breast Cancer: Results From a Preplanned monarchE Overall Survival Interim Analysis, Including 5-Year Efficacy Outcomes
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Adjuvant Abemaciclib Plus Endocrine Therapy for Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative, High-Risk Early Breast Cancer: Results From a Preplanned monarchE Overall Survival Interim Analysis, Including 5-Year Efficacy Outcomes.J Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun 10;42(17):2111. doi: 10.1200/JCO.24.00711. Epub 2024 Apr 30. J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38687953 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Erratum: Adjuvant Abemaciclib Plus Endocrine Therapy for Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative, High-Risk Early Breast Cancer: Results From a Preplanned monarchE Overall Survival Interim Analysis, Including 5-Year Efficacy Outcomes.J Clin Oncol. 2025 Jan;43(1):113. doi: 10.1200/JCO-24-02469. Epub 2024 Nov 19. J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39561312 No abstract available.
Abstract
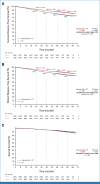
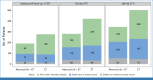
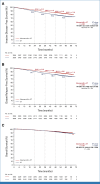
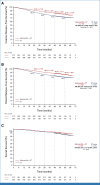
Clinical trials frequently include multiple end points that mature at different times. The initial report, typically based on the primary end point, may be published when key planned co-primary or secondary analyses are not yet available. Clinical trial updates provide an opportunity to disseminate additional results from studies, published in JCO or elsewhere, for which the primary end point has already been reported.Two years of adjuvant abemaciclib combined with endocrine therapy (ET) resulted in a significant improvement in invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) and distant relapse-free survival (DRFS) that persisted beyond the 2-year treatment period in patients with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative, node-positive, high-risk early breast cancer (EBC). Here, we report 5-year efficacy results from a prespecified overall survival (OS) interim analysis. In the intent-to-treat population, with a median follow-up of 54 months, the benefit of abemaciclib was sustained with hazard ratios of 0.680 (95% CI, 0.599 to 0.772) for IDFS and 0.675 (95% CI, 0.588 to 0.774) for DRFS. This persistence of abemaciclib benefit translated to continuous separation of the curves with a deepening in 5-year absolute improvement in IDFS and DRFS rates of 7.6% and 6.7%, respectively, compared with rates of 6% and 5.3% at 4 years and 4.8% and 4.1% at 3 years. With fewer deaths in the abemaciclib plus ET arm compared with the ET-alone arm (208 v 234), statistical significance was not reached for OS. No new safety signals were observed. In conclusion, abemaciclib plus ET continued to reduce the risk of developing invasive and distant disease recurrence beyond the completion of treatment. The increasing absolute improvement at 5 years is consistent with a carryover effect and further supports the use of abemaciclib in patients with high-risk EBC.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03155997.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures
References
-
- Sheffield KM, Peachey JR, Method M, et al. : A real-world US study of recurrence risks using combined clinicopathological features in HR-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer. Future Oncol 18:2667-2682, 2022 - PubMed
-
- NCCN : NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) for Breast Cancer V.4.2023. 2023. https://www.nccn.org/
-
- ESMO-MCBS : ESMO-MCBS Scorecards. 2023. https://www.esmo.org/guidelines/esmo-mcbs/esmo-mcbs-for-solid-tumours/es...
-
- Johnston SRD, Toi M, O'Shaughnessy J, et al. : Abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, node-positive, high-risk early breast cancer (monarchE): Results from a preplanned interim analysis of a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 24:77-90, 2023 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

