False aminoglycoside resistance in Enterobacterales and non-fermenters by an automated testing system: a descriptive study
- PMID: 38194628
- PMCID: PMC10790582
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.03093-23
False aminoglycoside resistance in Enterobacterales and non-fermenters by an automated testing system: a descriptive study
Abstract
Antimicrobial sensitivity data are important to guide antimicrobial therapy. In microbiological laboratories, routine sensitivity measurements are typically performed with automated testing systems such as VITEK2 and Phoenix. Using data from the Dutch national surveillance system for antimicrobial resistance over a 6-year period, we found that the measured minimum inhibitory concentrations for aminoglycosides in Enterobacterales and non-fermenters were too high for the Phoenix system. In addition, we observed a yearly increase in resistance for several species measured by Phoenix. These findings might have consequences for clinical treatment of patients with sepsis.
Keywords: aminoglycosides; antimicrobial susceptibility testing; automated testing system; gentamicin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
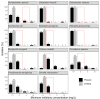
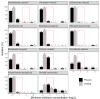
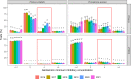
References
-
- The Dutch working party on antibiotic policy (SWAB) guideline for empirical Antibacterial therapy of sepsis in adults. 2020. Available from: https://swab.nl/exec/file/download/144 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli M, Coopersmith CM, French C, Machado FR, Mcintyre L, Ostermann M, Prescott HC, et al. . 2021. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Med 47:1181–1247. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06506-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- The European Committee on antimicrobial susceptibility testing - EUCAST. 2022. Available from: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_... - PMC - PubMed
-
- van der Kuil WA. 2021. Higher gentamicin resistance in Proteus spp. and Providencia spp. as measured by the Phoenix compared to the VITEK 2 automated antibiotic susceptibility test system, ESCMID poster 07/09/21, 239116, 3072
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

