Current perspectives on microglia-neuron communication in the central nervous system: Direct and indirect modes of interaction
- PMID: 38195039
- PMCID: PMC11674795
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.01.006
Current perspectives on microglia-neuron communication in the central nervous system: Direct and indirect modes of interaction
Abstract
Background: The incessant communication that takes place between microglia and neurons is essential the development, maintenance, and pathogenesis of the central nervous system (CNS). As mobile phagocytic cells, microglia serve a critical role in surveilling and scavenging the neuronal milieu to uphold homeostasis.
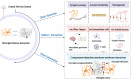
Aim of review: This review aims to discuss the various mechanisms that govern the interaction between microglia and neurons, from the molecular to the organ system level, and to highlight the importance of these interactions in the development, maintenance, and pathogenesis of the CNS.
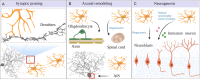
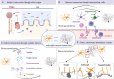
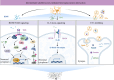
Key scientific concepts of review: Recent research has revealed that microglia-neuron interaction is vital for regulating fundamental neuronal functions, such as synaptic pruning, axonal remodeling, and neurogenesis. The review will elucidate the intricate signaling pathways involved in these interactions, both direct and indirect, to provide a better understanding of the fundamental mechanisms of brain function. Furthermore, gaining insights into these signals could lead to the development of innovative therapies for neural disorders.
Keywords: CNS; Interaction; Microglia; Molecular mechanisms; Neuroinflammation; Neuron.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bidirectional microglia-neuron communication in the healthy brain.Neural Plast. 2013;2013:456857. doi: 10.1155/2013/456857. Epub 2013 Sep 2. Neural Plast. 2013. PMID: 24078884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia-neuron crosstalk: Signaling mechanism and control of synaptic transmission.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Oct;94:138-151. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2019.05.017. Epub 2019 May 30. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31112798 Review.
-
Crosstalk between Microglia and Neurons in Neurotrauma: An Overview of the Underlying Mechanisms.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(11):2050-2065. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666211202123322. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34856905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of microglia in the central nervous system--beyond the immune response.Neuron Glia Biol. 2011 Feb;7(1):47-53. doi: 10.1017/S1740925X12000063. Epub 2012 May 22. Neuron Glia Biol. 2011. PMID: 22613055 Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles and intercellular communication in the central nervous system.FEBS Lett. 2021 May;595(10):1391-1410. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14074. Epub 2021 Apr 3. FEBS Lett. 2021. PMID: 33728650 Review.
Cited by
-
Microglial process convergence onto injured axonal swellings, a human postmortem brain tissue study.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 9:rs.3.rs-4713316. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4713316/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 12;14(1):21369. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71312-7. PMID: 39149456 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The role of microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: from the perspective of ferroptosis.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Apr 30. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01560-4. Online ahead of print. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40307457 Review.
-
Neuroimmune crosstalk in chronic neuroinflammation: microglial interactions and immune modulation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2025 Apr 7;19:1575022. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1575022. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40260075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolin-1 negatively regulates the calcitonin receptor-like receptor and neuroinflammation in a female mouse model of migraine.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 May 21;22(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03466-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 40399967 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Restore Endothelial Integrity and Alleviate Emotional Impairments in a Diabetic Mouse Model via Inhibition of MMP-9 Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 3;26(7):3355. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073355. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biber K., Vinet J., Boddeke H.W. Neuron-microglia signaling: chemokines as versatile messengers. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;198:69–74. - PubMed
-
- Biber K., Neumann H., Inoue K., Boddeke H.W. Neuronal 'On' and 'Off' signals control microglia. Trends Neurosci. 2007;30:596–602. - PubMed
-
- Pósfai B., Cserép C., Orsolits B., Dénes Á. New Insights into Microglia-Neuron Interactions: A Neuron's Perspective. Neuroscience. 2019;405:103–117. - PubMed
-
- Nonaka S., Nakanishi H. Microglial clearance of focal apoptotic synapses. Neurosci Lett. 2019;707 - PubMed
-
- Bruce-Keller A.J. Microglial-neuronal interactions in synaptic damage and recovery. J Neurosci Res. 1999;58:191–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

