Outcomes after distal pancreatectomy with or without splenectomy for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: international multicentre cohort study
- PMID: 38195084
- PMCID: PMC10776207
- DOI: 10.1093/bjs/znad424
Outcomes after distal pancreatectomy with or without splenectomy for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: international multicentre cohort study
Abstract
Background: International guidelines on intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) recommend a formal oncological resection including splenectomy when distal pancreatectomy is indicated. This study aimed to compare oncological and surgical outcomes after distal pancreatectomy with or without splenectomy in patients with presumed IPMN.
Methods: An international, retrospective cohort study was undertaken in 14 high-volume centres from 7 countries including consecutive patients after distal pancreatectomy for IPMN (2005-2019). Patients were divided into spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy (SPDP) and distal pancreatectomy with splenectomy (DPS). The primary outcome was lymph node metastasis (LNM). Secondary outcomes were overall survival, duration of operation, blood loss, and secondary splenectomy.
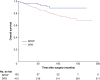
Results: Overall, 700 patients were included after distal pancreatectomy for IPMN; 123 underwent SPDP (17.6%) and 577 DPS (82.4%). The rate of malignancy was 29.6% (137 patients) and the overall rate of LNM 6.7% (47 patients). Patients with preoperative suspicion of malignancy had a LNM rate of 17.2% (23 of 134) versus 4.3% (23 of 539) among patients without suspected malignancy (P < 0.001). Overall, SPDP was associated with a shorter operating time (median 180 versus 226 min; P = 0.001), less blood loss (100 versus 336 ml; P = 0.001), and shorter hospital stay (5 versus 8 days; P < 0.001). No significant difference in overall survival was observed between SPDP and DPS for IPMN after correction for prognostic factors (HR 0.50, 95% c.i. 0.22 to 1.18; P = 0.504).
Conclusion: This international cohort study found LNM in 6.7% of patients undergoing distal pancreatectomy for IPMN. In patients without preoperative suspicion of malignancy, SPDP seemed oncologically safe and was associated with improved short-term outcomes compared with DPS.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of BJS Foundation Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
J.E.v.H. currently has a role as independent observer for Olympus and has received honoraria from Cook Medical, Boston Scientific, Metronic, and Abbvie. The authors declare no other conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.Gland Surg. 2024 Sep 30;13(9):1665-1669. doi: 10.21037/gs-24-150. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Gland Surg. 2024. PMID: 39421054 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Berland LL, Silverman SG, Gore RM, Mayo-Smith WW, Megibow AJ, Yee J et al. Managing incidental findings on abdominal CT: white paper of the ACR incidental findings committee. J Am Coll Radiol 2010;7:754–773 - PubMed
-
- van Huijgevoort NCM, Del Chiaro M, Wolfgang CL, van Hooft JE, Besselink MG. Diagnosis and management of pancreatic cystic neoplasms: current evidence and guidelines. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;16:676–689 - PubMed
-
- Kromrey ML, Bulow R, Hubner J, Paperlein C, Lerch MM, Ittermann T et al. Prospective study on the incidence, prevalence and 5-year pancreatic-related mortality of pancreatic cysts in a population-based study. Gut 2018;67:138–115 - PubMed
-
- Tanaka M, Fernandez-Del Castillo C, Kamisawa T, Jang JY, Levy P, Ohtsuka T et al. Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2017;17:738–753 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

