Evolution of cell therapy for renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38195534
- PMCID: PMC10775455
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-023-01911-x
Evolution of cell therapy for renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
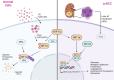
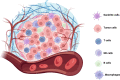
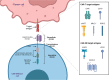
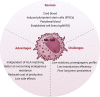
Treatment for renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has improved dramatically over the last decade, shifting from high-dose cytokine therapy in combination with surgical resection of tumors to targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and combination therapies. However, curative treatment, particularly for advanced-stage disease, remains rare. Cell therapy as a "living drug" has achieved hematological malignancy cures with a high response rate, and significant research efforts have been made to facilitate its translation to solid tumors. Herein, we overview the cellular therapies for RCC focusing on allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, T cell receptor gene-modified T cells, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, CAR natural killer (NK) cells, lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cells, γδ T cells, and dendritic cell vaccination. We have also included perspectives for using other recent approaches, such as CAR macrophages, dendritic cell-cytokine induced killer cells and regulatory CAR-T cells to shed light on preclinical development of cell therapy and advancing cell therapy into clinic to achieve cures for RCC.
Keywords: CAR-NK; CAR-T; Cell therapy; Immunotherapy; Renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ruf M, Mittmann C, Nowicka AM, Hartmann A, Hermanns T, Poyet C, et al. pVHL/HIF-regulated CD70 expression is associated with infiltration of CD27 + lymphocytes and increased serum levels of soluble CD27 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:889–898. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-14-1425. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

