Management and treatment outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis in the era of biologic and targeted synthetic therapies: evaluation of 10-year data from the KURAMA cohort
- PMID: 38195572
- PMCID: PMC10775516
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-023-03251-z
Management and treatment outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis in the era of biologic and targeted synthetic therapies: evaluation of 10-year data from the KURAMA cohort
Abstract
Background: Advances in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment, highlighted by biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) and targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs), have altered the paradigm of RA treatment in the last decade. Therefore, real-world clinical evidence is needed to understand how treatment strategies and outcomes have changed.
Methods: Using an observational cohort of RA from 2012 to 2021, we collected cross-sectional data of RA patients annually to analyze a trend in RA management. For patients who initiated b/tsDMRDs, we evaluated treatment outcomes between b/tsDMARDs. Mixed-effect models were applied to examine the statistical implications of changes over time in treatment outcomes with a background adjustment.
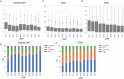
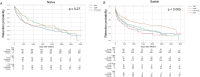
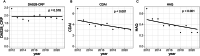
Results: We analyzed annual cross-sectional data from 5070 patients and longitudinal data from 1816 patients in whom b/tsDMARDs were initiated between 2012 and 2021. b/tsDMARD use increased, whereas glucocorticoid use decreased from 2012 to 2021. Disease activity and functional disability measures improved over time. The percentage of tsDMARD prescriptions considerably increased. All b/tsDMARDs showed clinical improvements in disease activity and functional disability. Statistically, TNFi showed better short-term improvements in b/tsDMARD-naïve patients, while IL6Ri demonstrated significant long-term benefits. IL6Ri had better retention rates in switched patients. After adjustment for patient characteristics, the annual change of RA disease activity and functional disability fared significantly better from 2012 to 2021.
Conclusions: With the development of new RA therapeutics, overall treatment outcomes advanced in the past decade.
Keywords: Biologics; Cohort study; JAK inhibitors; Rheumatoid arthritis; Treatment outcomes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The Department of Advanced Medicine for Rheumatic Diseases, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, is supported by Nagahama City, Shiga, Japan; Toyooka City, Hyogo, Japan; Asahi Kasei Pharma Corp.; and AYUMI Pharmaceutical Co. The KURAMA cohort study is supported by a grant from Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. Takayuki.F. speaker fees from AbbVie GK, Asahi Kasei Pharma Corp., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., and Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K. Kos.M. received speaker’s fees and/or consulting fees from Eisai Co. Ltd, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Pfizer Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, UCB Japan Co. Ltd, Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., and Astellas Pharma Inc. H.O. has received speaker fees from AbbVie, Asahi Kasei, Astellas Pharma Inc., Eisai Co. Ltd., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, and Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. A.O. has received research grants and/or speaker fees from Pfizer Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb., Advantest, Asahi Kasei Pharma Corp., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K, Ono Pharmaceutical Co., UCB Japan Co., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Eisai Co. Ltd., Abbvie Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. K.N. received a speaking fee and/or consulting fees from Asahi Kasei Pharma Corp., Ayumi Pharmaceutical Co, Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd, Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co.,Inc, and Kyocera. M.H. received research grants and/or speaker fees from Abbvie, Asahi Kasei, Astellas, Ayumi, Brystol Meyers, Chugai, EA Pharma, Eisai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Novartis Pharma, and Tanabe Mitsubishi. R.W. has received a research grant from AbbVie and speaker’s fee from Asahi Kasei, Chugai, Eli Lilly, and GSK. M.T. received research grants and/or speaker fees from AbbVie GK, Asahi Kasei Pharma Corp., Astellas Pharma Inc., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., Pfizer Inc., Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Tanabe Mitsubishi Pharma Corp., Teijin Pharma, Ltd., UCB Japan Co., Ltd. Koi.M. received a speaking fee and/or consulting fees from Eisai Co. Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.; Asahi Kasei Pharma Corp., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K. and Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. S. M. received speaker fees from Pfizer Inc. A.M. has received honorarium from AbbVie G.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Eisai Co. Ltd., Pfizer Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Astellas Pharma Inc., and Gilead Sciences Japan., and has received research grants from AbbVie G.K., Asahi Kasei Pharma Corp., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co. and Eisai Co. Ltd. Takao.F. has received lecture fees or honoraria from AbbVie GK; Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation; Astellas Pharma Inc.; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.; Eisai Co. Ltd.; Eli Lilly Japan K.K.; Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K.; Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation; Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.; and Pfizer Japan Inc.; has received grants from AbbVie GK; Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.; Eisai Co. Ltd.; and Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation. T.M. received speaker’s fee from Asahi Kasei Pharma, AbbVie, Eisai, Jansen Mitsubishi Tanabe, Taisho, and Pfizer. H.I. has received a research grant and/or speaker fee from Bristol-Myers Squibb. The other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

