Diagnostic accuracy of barium enema versus full-thickness rectal biopsy in children with clinically suspected Hirschsprung's disease: A comparative cross-sectional study
- PMID: 38196566
- PMCID: PMC10774491
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.1798
Diagnostic accuracy of barium enema versus full-thickness rectal biopsy in children with clinically suspected Hirschsprung's disease: A comparative cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background and aims: Hirschsprung's disease (HSD) remains a common cause of pediatric intestinal obstruction. Barium contrast enema (BE) is the primary imaging modality for the evaluation of clinically suspected cases. Here, we aimed to assess the diagnostic accuracy of BE in children with clinically suspected HSD when compared to a gold standard full-thickness rectal biopsy (FTRB).
Methods: We recruited and consecutively enrolled children with clinically suspected HSD at two tertiary teaching hospitals. Participants underwent BE imaging and two radiologists interpreted the findings independently. Participants further underwent FTRB by pediatric surgeons as the confirmatory test. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and receiver operating characteristics (ROC) with the area under the curve (AUC) were calculated on Stata version 14.2, taking FTRB as the standard.
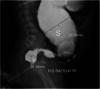
Results: We enrolled 55 cases, of which 49 completed the evaluation and were included in the final analysis. The median age was 9.4 months (interquartile range: 2-24], with a male-to-female ratio of 4.4:1. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of BE were 0.95 (95% confidence interval [CI] [0.81-0.99]), 0.73 (95% CI [0.39-0.94]), 0.92 (95% CI [0.82-0.97]), and 0.80 (95% CI [0.50-0.94]), respectively. On AUC, the diagnostic accuracy of BE compared to the confirmatory FTRB was 0.84 (95% CI [0.69-0.98]). The diagnostic accuracy was higher in neonates (ROC: 1.00) when compared to infants (ROC: 0.83) or those above 1 year of age (ROC: 0.798). HSD-suggestive BE findings were associated with absence of ganglion cells on FTRB (χ 2 = 23.301, p < 0.001). Inverted rectosigmoid ratio and transition zone were more sensitive in detecting HSD of 0.92 (95% CI [0.74-0.98]) and 0.81 (95% CI [0.63-0.92]), respectively.
Conclusion: BE is sufficiently accurate in the diagnosis of children with HSD, suggesting BE would likely be used to inform surgical management in settings where confirmatory biopsy is lacking. However, clinical judgment is warranted in interpreting negative BE findings.
Keywords: Ethiopia; Hirschsprung's disease; aganglionosis; barium enema; diagnostic accuracy; rectal biopsy.
© 2024 The Authors. Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Huerta CT, Ramsey WA, Davis JK, et al. Nationwide outcomes of newborns with rectosigmoid versus long‐segment Hirschsprung disease. J Pediatr Surg. 2023;58:849‐855. - PubMed
-
- Beltman L, Labib H, Masselink M, et al. Diagnosing Hirschsprung disease in children younger than 6 months of age: insights in incidence of complications of rectal suction biopsy and other final diagnoses. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2023;33:360‐366. - PubMed
-
- Trinidad S, Kayima P, Kotecha V, et al. Hirschsprung's disease in low‐and middle‐income countries. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2022;31:151163. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

