A bi-criterion sequence-dependent scheduling problem with order deliveries
- PMID: 38196963
- PMCID: PMC10773847
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1763
A bi-criterion sequence-dependent scheduling problem with order deliveries
Abstract
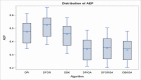
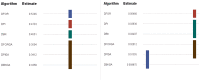
The manufacturing sector faces unprecedented challenges, including intense competition, a surge in product varieties, heightened customization demands, and shorter product life cycles. These challenges underscore the critical need to optimize manufacturing systems. Among the most enduring and complex challenges within this domain is production scheduling. In practical scenarios, setup time is whenever a machine transitions from processing one product to another. Job scheduling with setup times or associated costs has garnered significant attention in both manufacturing and service environments, prompting extensive research efforts. While previous studies on customer order scheduling primarily focused on orders or jobs to be processed across multiple machines, they often overlooked the crucial factor of setup time. This study addresses a sequence-dependent bi-criterion scheduling problem, incorporating order delivery considerations. The primary objective is to minimize the linear combination of the makespan and the sum of weighted completion times of each order. To tackle this intricate challenge, we propose pertinent dominance rules and a lower bound, which are integral components of a branch-and-bound methodology employed to obtain an exact solution. Additionally, we introduce a heuristic approach tailored to the problem's unique characteristics, along with three refined variants designed to yield high-quality approximate solutions. Subsequently, these three refined approaches serve as seeds to generate three distinct populations or chromosomes, each independently employed in a genetic algorithm to yield a robust approximate solution. Ultimately, we meticulously assess the efficacy of each proposed algorithm through comprehensive simulation trials.
Keywords: Bi-criterion; Branch-and-bound; Customer order scheduling; Genetic algorithm; Makespan; Scheduling; Sequence-dependent; Setup time; Single-machine; Weighted completion times.
©2024 Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Allahverdi A. The third comprehensive survey on scheduling problems with setup times/costs. European Journal of Operational Research. 2015;246(2):345–378. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2015.04.004. - DOI
-
- Allahverdi A, Gupta JND, Aldowaisan T. A review of scheduling research involving setup considerations. Omega. 1999;27(2):219–239. doi: 10.1016/S0305-0483(98)00042-5. - DOI
-
- Allahverdi A, Ng CT, Cheng TCE, Kovalyov MY. A survey of scheduling problems with setup times or costs. European Journal of Operational Research. 2008;187:985–1032. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2006.06.060. - DOI
-
- Allahverdi A, Soroush HM. The significance of reducing setup times/setup costs. European Journal of Operational Research. 2008;187:978–984. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2006.09.010. - DOI
-
- de Athayde Prata B, Rodrigues CD, Framinan JM. Customer order scheduling problem to minimize makespan with sequence-dependent setup times. Computers & Industrial Engineering. 2021a;151:106962. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2020.106962. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
