Effectiveness of Drug Repurposing and Natural Products Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 38197085
- PMCID: PMC10773251
- DOI: 10.2147/CPAA.S429064
Effectiveness of Drug Repurposing and Natural Products Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
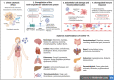
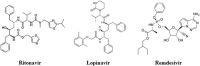
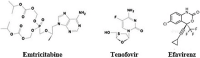
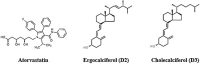
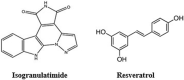
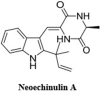
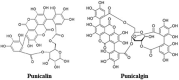
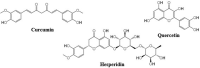
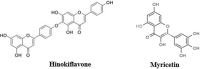
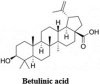
The Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a betacoronavirus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, causing respiratory disorders, and even death in some individuals, if not appropriately treated in time. To face the pandemic, preventive measures have been taken against contagions and the application of vaccines to prevent severe disease and death cases. For the COVID-19 treatment, antiviral, antiparasitic, anticoagulant and other drugs have been reused due to limited specific medicaments for the disease. Drug repurposing is an emerging strategy with therapies that have already tested safe in humans. One promising alternative for systematic experimental screening of a vast pool of compounds is computational drug repurposing (in silico assay). Using these tools, new uses for approved drugs such as chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin, zidovudine, ribavirin, lamivudine, remdesivir, lopinavir and tenofovir/emtricitabine have been conducted, showing effectiveness in vitro and in silico against SARS-CoV-2 and some of these, also in clinical trials. Additionally, therapeutic options have been sought in natural products (terpenoids, alkaloids, saponins and phenolics) with promising in vitro and in silico results for use in COVID-19 disease. Among these, the most studied are resveratrol, quercetin, hesperidin, curcumin, myricetin and betulinic acid, which were proposed as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors. Among the drugs reused to control the SARS-CoV2, better results have been observed for remdesivir in hospitalized patients and outpatients. Regarding natural products, resveratrol, curcumin, and quercetin have demonstrated in vitro antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and in vivo, a nebulized formulation has demonstrated to alleviate the respiratory symptoms of COVID-19. This review shows the evidence of drug repurposing efficacy and the potential use of natural products as a treatment for COVID-19. For this, a search was carried out in PubMed, SciELO and ScienceDirect databases for articles about drugs approved or under study and natural compounds recognized for their antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: COVID-19; coronavirus; medicinal plants; pandemic.
© 2024 Velásquez et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
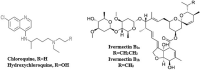
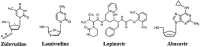
Similar articles
-
Antiviral Efficacies of FDA-Approved Drugs against SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Ferrets.mBio. 2020 May 22;11(3):e01114-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01114-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32444382 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Ivermectin, Chloroquine/Hydroxychloroquine, and Azithromycin in Managing COVID-19: A Systematic Review of Phase III Clinical Trials.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 27;12(10):2206. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102206. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into antiviral mechanisms of remdesivir, lopinavir/ritonavir and chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine affecting the new SARS-CoV-2.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;131:110668. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110668. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32861965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational drug discovery and repurposing for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Jan;106:104490. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104490. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 33261845 Free PMC article.
-
Broad Anti-coronavirus Activity of Food and Drug Administration-Approved Drugs against SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro and SARS-CoV In Vivo.J Virol. 2020 Oct 14;94(21):e01218-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01218-20. Print 2020 Oct 14. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32817221 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Trans-Cannabitriol as a Dual Inhibition of MPOX Adhesion Receptors L1R and E8L: An In Silico Perspective.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2025 Jul 23;19:11779322251355315. doi: 10.1177/11779322251355315. eCollection 2025. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2025. PMID: 40718062 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons learnt from broad-spectrum coronavirus antiviral drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2024 Sep;19(9):1023-1041. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2024.2385598. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 39078037 Review.
-
Arylamines QSAR-Based Design and Molecular Dynamics of New Phenylthiophene and Benzimidazole Derivatives with Affinity for the C111, Y268, and H73 Sites of SARS-CoV-2 PLpro Enzyme.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 9;17(5):606. doi: 10.3390/ph17050606. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794177 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Polymerase Inhibitor Enisamium for Treatment of Moderate COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter, Double-Blind Phase 3 Clinical Trial.Adv Respir Med. 2024 May 6;92(3):202-217. doi: 10.3390/arm92030021. Adv Respir Med. 2024. PMID: 38804439 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
What is the role of microbial biotechnology and genetic engineering in medicine?Microbiologyopen. 2024 Apr;13(2):e1406. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1406. Microbiologyopen. 2024. PMID: 38556942 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Manta B, Sarkisian AG. Fisiopatología de la enfermedad COVID-19. Odontoestomatologia. 2022;24:1–19. doi:10.22592/ode2022n39e312 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

