Mutations upstream from sdaC and malT in Escherichia coli uncover a complex interplay between the cAMP receptor protein and different sigma factors
- PMID: 38197669
- PMCID: PMC10882989
- DOI: 10.1128/jb.00355-23
Mutations upstream from sdaC and malT in Escherichia coli uncover a complex interplay between the cAMP receptor protein and different sigma factors
Abstract
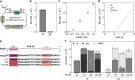
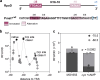
In Escherichia coli, one of the best understood microorganisms, much can still be learned about the basic interactions between transcription factors and promoters. When a cAMP-deficient cya mutant is supplied with maltose as the main carbon source, mutations develop upstream from the two genes malT and sdaC. Here, we explore the regulation of the two promoters, using fluorescence-based genetic reporters in combination with both spontaneously evolved and systematically engineered cis-acting mutations. We show that in the cya mutant, regulation of malT and sdaC evolves toward cAMP-independence and increased expression in the stationary phase. Furthermore, we show that the location of the cAMP receptor protein (Crp) binding site upstream of malT is important for alternative sigma factor usage. This provides new insights into the architecture of bacterial promoters and the global interplay between Crp and sigma factors in different growth phases.IMPORTANCEThis work provides new general insights into (1) the architecture of bacterial promoters, (2) the importance of the location of Class I Crp-dependent promoters, and (3) the global interplay between Crp and sigma factors in different growth phases.
Keywords: cAMP receptor protein Crp/Cap; sigma factors; stationary phase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Positive Effect of Carbon Sources on Natural Transformation in Escherichia coli: Role of Low-Level Cyclic AMP (cAMP)-cAMP Receptor Protein in the Derepression of rpoS.J Bacteriol. 2015 Oct;197(20):3317-28. doi: 10.1128/JB.00291-15. Epub 2015 Aug 10. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26260461 Free PMC article.
-
Complex transcriptional control of the sigma s-dependent stationary-phase-induced and osmotically regulated osmY (csi-5) gene suggests novel roles for Lrp, cyclic AMP (cAMP) receptor protein-cAMP complex, and integration host factor in the stationary-phase response of Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(24):7910-7. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.24.7910-7917.1993. J Bacteriol. 1993. PMID: 8253679 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of the regulation of csiD, a carbon starvation-inducible gene in Escherichia coli that is exclusively dependent on sigma s and requires activation by cAMP-CRP.J Mol Biol. 1998 Feb 20;276(2):339-53. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1533. J Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9512707
-
Control of rpoS transcription in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas: why so different?Mol Microbiol. 2003 Jul;49(1):1-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03547.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12823806 Review.
-
cAMP Activation of the cAMP Receptor Protein, a Model Bacterial Transcription Factor.J Microbiol. 2023 Mar;61(3):277-287. doi: 10.1007/s12275-023-00028-6. Epub 2023 Mar 9. J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36892777 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

