Effect of BMI on cumulative live birth rates in patients that completed IVF treatment: a retrospective cohort study of 16,126 patients
- PMID: 38197872
- PMCID: PMC10895320
- DOI: 10.1530/EC-23-0105
Effect of BMI on cumulative live birth rates in patients that completed IVF treatment: a retrospective cohort study of 16,126 patients
Abstract
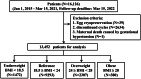
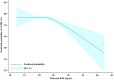
Although several studies have reported that high maternal BMI could influence the cumulative live birth rate (CLBR) in fresh embryo transfer cycles, the association of BMI with CLBR remains unclear in patients that completed IVF treatment. In this study, we examined the association of maternal BMI with CLBR, including repetitive one oocyte pick-up (OPU) and all fresh and frozen embryo transfer until live birth or embryos were run out. A total of 16,126 patients' data were included in the analysis and were divided into four groups based on BMI. We found that patients' characteristics, embryo parameters, and pregnancy outcomes differed among different BMI groups. Multivariate logistic regression showed that being underweight was associated with a higher possibility of having live birth than the reference group (OR (95% CI) 1.40 (1.22-1.59), P < 0.001), whereas being overweight and obese were associated with a lower possibility of having live birth than the reference group ((OR (95% CI) 0.81 (0.74-0.90), P < 0.001) and (OR (95% CI) 0.68 (0.55-0.85), P < 0.001)). After adjustment for confounding factors, the reference group was associated with a higher possibility of having live birth, with a significant difference found between the obese and reference groups (OR (95% CI) 0.55 (0.43-0.70), P < 0.001). An association was found between CLBR and BMI, indicating that an increase in BMI results in a decline in CLBR. Moreover, the CLBR of patients with different characteristics differed in the various BMI groups. Taken together, our data show that maternal BMI has a significant impact on CLBR.
Keywords: body mass index; cumulative live birth rate; in vitro fertilization; obesity; overweight.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no relevant financial or nonfinancial competing interests to report.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

