Analysis of Isotretinoin-Induced Alterations in the Levels of Plasma Trace Elements: Investigation of the Relationship Between Magnesium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Zinc, and Treatment-Related Side Effects
- PMID: 38197903
- PMCID: PMC11442544
- DOI: 10.1007/s12011-023-04053-9
Analysis of Isotretinoin-Induced Alterations in the Levels of Plasma Trace Elements: Investigation of the Relationship Between Magnesium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Zinc, and Treatment-Related Side Effects
Abstract
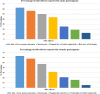
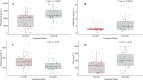
Isotretinoin is an effective treatment against acne vulgaris, but it also causes many side effects during and after the treatment. The relationship between the changes in the levels of plasma trace elements of patients with AV after 3 months of isotretinoin treatment and the side effects was investigated in the study. Plasma samples of 35 patients were collected before and after isotretinoin treatment. Samples were analyzed by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometer. After treatment, the levels of phosphorus, magnesium, and zinc in plasma increased statistically, while the level of potassium decreased (p < 0.05). The treatment had differing effects on zinc levels based on the gender of the individuals. With treatment, the levels of zinc in the plasma of men showed a greater increase compared to women (p = 7.3e-04). Additionally, the correlation matrix analysis revealed a strong correlation (R > 0.8) between magnesium and calcium. According to the study results, the change in phosphorus and potassium levels shows that isotretinoin affects kidney functions. The results suggest that phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, and zinc are associated with fatigue, dry skin and chapped lips, hair loss, and sebum secretion, respectively. Consequently, the study emphasizes the need for a comprehensive pre-treatment assessment, including monitoring of liver and kidney function as well as the levels of phosphorus and potassium in patients.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Changes of plasma amino acid levels and metabolic pathways in isotretinoin therapy: ınsights into managing acne vulgaris side effects.Arch Dermatol Res. 2025 Mar 17;317(1):591. doi: 10.1007/s00403-025-04106-0. Arch Dermatol Res. 2025. PMID: 40097819
-
The relationship between erythrocyte zinc levels and isotretinoin use in acne vulgaris patients.Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2015;34(4):303-6. doi: 10.3109/15569527.2014.979426. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25373485
-
Evaluation of the changes in sebum, moisturization and elasticity in acne vulgaris patients receiving systemic isotretinoin treatment.Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2021 Jun;40(2):140-144. doi: 10.1080/15569527.2021.1922434. Epub 2021 May 12. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33978534 Clinical Trial.
-
Vitamin D levels in acne vulgaris patients treated with oral isotretinoin.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019 Feb;18(1):16-20. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12503. Epub 2018 Feb 20. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 29460332 Review.
-
Effects of isotretinoin on glucose metabolism in patients with acne: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2020 Jun;18(6):539-545. doi: 10.1111/ddg.14108. Epub 2020 May 11. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2020. PMID: 32391951
Cited by
-
Changes of plasma amino acid levels and metabolic pathways in isotretinoin therapy: ınsights into managing acne vulgaris side effects.Arch Dermatol Res. 2025 Mar 17;317(1):591. doi: 10.1007/s00403-025-04106-0. Arch Dermatol Res. 2025. PMID: 40097819
-
Combination of Botulinum Toxin A and Hyaluronic Acid Improved Facial Pore Enlargement Caused by Acne.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Apr;24(4):e70198. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70198. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40271965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ibrahim MA, Mohammed SA, Elhabak DM (2021) Role of KLF2: new insight in inflammatory acne pathogenesis. J Cosmet Dermatol 20:964–970. 10.1111/JOCD.13595 - PubMed
-
- Chitturi R, Baddam VR, Prasad L et al (2015) A review on role of essential trace elements in health and disease. J Dr NTR Univ Heal Sci 4:75. 10.4103/2277-8632.158577
-
- Shayganfard M (2021) Are essential trace elements effective in modulation of mental disorders? Update and perspectives. Biol Trace Elem Res 2021 2003 200:1032–1059. 10.1007/S12011-021-02733-Y - PubMed
-
- Bilgiç Ö, Altinyazar HC, Sivrikaya A, Ünlü A (2014) The relationship between erythrocyte zinc levels and isotretinoin use in acne vulgaris patients. 34:303–306. 10.3109/15569527.2014.979426 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

