Inborn errors of immunity with kidney and urinary tract disorders: a review
- PMID: 38198013
- PMCID: PMC11090940
- DOI: 10.1007/s11255-023-03907-4
Inborn errors of immunity with kidney and urinary tract disorders: a review
Abstract
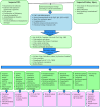
Human inborn errors of immunity (IEIs), previously referred to as primary immunodeficiency disorders (PIDs), are a heterogeneous spectrum of inherited abnormalities of the immune system with different organ involvement. The number of identified IEIs is rapidly increasing, highlighting the non-negligible role of an interdisciplinary approach in clinical diagnosis. Kidney disorders are one of the important comorbidities in some of the affected patients and play a significant role in the diagnosis and course of disease. According to recent studies, 22 types of human IEI with renal manifestations have been identified so far, including immunodeficiency with congenital thrombocytopenia, thymic defects with additional congenital anomalies, complement deficiencies, type 1 interferonopathies, immunity related to non-hematopoietic tissues, congenital neutropenia's, common variable immunodeficiency disorder (CVID) phenotype and immuno-osseous dysplasia. Based on this classification, we herein review IEIs with renal features and explain the genetic defect, inheritance, and type of renal manifestations.
Keywords: Inborn error of immunity; Kidney; Nephropathy; Primary immunodeficiency; Renal disorder.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Tangye SG, Al-Herz W, Bousfiha A, Cunningham-Rundles C, Franco JL, Holland SM, et al. Human Inborn Errors of Immunity: 2022 Update on the Classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee. J Clin Immunol. 2022;42(7):1473–1507. doi: 10.1007/s10875-022-01289-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical