Severe esophagitis induced by antituberculosis drugs: a case report
- PMID: 38198375
- PMCID: PMC10768651
- DOI: 10.1590/S1678-9946202466002
Severe esophagitis induced by antituberculosis drugs: a case report
Abstract
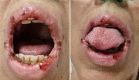
Tuberculosis stands as one of humanity's oldest afflictions, intrinsically intertwined with social disparities. This formidable disease spares no age group and remains the prevailing cause of infection-induced mortality worldwide, particularly in developing nations. We present a case of a 56-year-old woman with diabetes who was diagnosed with Pulmonary Tuberculosis. After receiving antituberculosis drugs as part of her treatment, she experienced a range of systemic manifestations and suffered from severe ulcerative esophagitis. This adverse reaction led to uncontrollable gastrointestinal intolerance, tragically resulting in her untimely demise. The incident underscores the potential seriousness of adverse reactions that can arise from tuberculosis treatment medications.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Forget EJ, Menzies D. Adverse reactions to first-line antituberculosis drugs. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2006;5:231–249. - PubMed
-
- Brasil. Ministério de Saúde. Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. Departamento de Vigilância das Doenças Transmissíveis . Manual de recomendações para o controle da tuberculose no Brasil. 2. Brasília: Ministério da Saúde; 2019. [cited 2023 Nov 22]. https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/manual_recomendacoes_controle... .
-
- Lange P, Oun H, Fuller S, Turney JH. Eosinophilic colitis due to rifampicin. Lancet. 1994;344:1296–1297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

