Breakthrough infections by SARS-CoV-2 variants boost cross-reactive hybrid immune responses in mRNA-vaccinated Golden Syrian hamsters
- PMID: 38198521
- PMCID: PMC10805310
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011805
Breakthrough infections by SARS-CoV-2 variants boost cross-reactive hybrid immune responses in mRNA-vaccinated Golden Syrian hamsters
Abstract
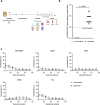
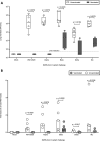
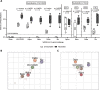
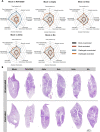
Hybrid immunity (vaccination + natural infection) to SARS-CoV-2 provides superior protection to re-infection. We performed immune profiling studies during breakthrough infections in mRNA-vaccinated hamsters to evaluate hybrid immunity induction. The mRNA vaccine, BNT162b2, was dosed to induce binding antibody titers against ancestral spike, but inefficient serum virus neutralization of ancestral SARS-CoV-2 or variants of concern (VoCs). Vaccination reduced morbidity and controlled lung virus titers for ancestral virus and Alpha but allowed breakthrough infections in Beta, Delta and Mu-challenged hamsters. Vaccination primed for T cell responses that were boosted by infection. Infection back-boosted neutralizing antibody responses against ancestral virus and VoCs. Hybrid immunity resulted in more cross-reactive sera, reflected by smaller antigenic cartography distances. Transcriptomics post-infection reflects both vaccination status and disease course and suggests a role for interstitial macrophages in vaccine-mediated protection. Therefore, protection by vaccination, even in the absence of high titers of neutralizing antibodies in the serum, correlates with recall of broadly reactive B- and T-cell responses.
Copyright: © 2024 Diego et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: the M.S. laboratory has received unrelated research funding in sponsored research agreements from ArgenX BV, Moderna, 7Hills Pharma and Phio Pharmaceuticals which has no competing interest with this work. The A.G.-S. laboratory has received research support from GSK, Pfizer, Senhwa Biosciences, Kenall Manufacturing, Blade Therapeutics, Avimex, Johnson & Johnson, Dynavax, 7Hills Pharma, Pharmamar, ImmunityBio, Accurius, Nanocomposix, Hexamer, N-fold LLC, Model Medicines, Atea Pharma, Applied Biological Laboratories and Merck, outside of the reported work. A.G.-S. has consulting agreements for the following companies involving cash and/or stock: Castlevax, Amovir, Vivaldi Biosciences, Contrafect, 7Hills Pharma, Avimex, Pagoda, Accurius, Esperovax, Farmak, Applied Biological Laboratories, Pharmamar, CureLab Oncology, CureLab Veterinary, Synairgen, Paratus and Pfizer, outside of the reported work. A.G.-S. has been an invited speaker in meeting events organized by Seqirus, Janssen, Abbott and Astrazeneca. A.G.-S. is inventor on patents and patent applications on the use of antivirals and vaccines for the treatment and prevention of virus infections and cancer, owned by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, outside of the reported work.
Figures


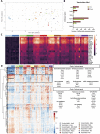
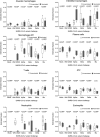
Update of
-
Breakthrough infections by SARS-CoV-2 variants boost cross-reactive hybrid immune responses in mRNA-vaccinated Golden Syrian Hamsters.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 23:2023.05.22.541294. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.22.541294. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jan 10;20(1):e1011805. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011805. PMID: 37425792 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Breakthrough infections by SARS-CoV-2 variants boost cross-reactive hybrid immune responses in mRNA-vaccinated Golden Syrian Hamsters.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 23:2023.05.22.541294. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.22.541294. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jan 10;20(1):e1011805. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011805. PMID: 37425792 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Prototype and BA.5 protein nanoparticle vaccines protect against Omicron BA.5 variant in Syrian hamsters.J Virol. 2024 Mar 19;98(3):e0120623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01206-23. Epub 2024 Feb 2. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38305154 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV2 variant-specific replicating RNA vaccines protect from disease following challenge with heterologous variants of concern.Elife. 2022 Feb 22;11:e75537. doi: 10.7554/eLife.75537. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35191378 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralizing antibody responses elicited by SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination wane over time and are boosted by breakthrough infection.Sci Transl Med. 2022 Mar 23;14(637):eabn8057. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abn8057. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Sci Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35166573 Free PMC article.
-
Infection-mediated immune response in SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infection and implications for next-generation COVID-19 vaccine development.Vaccine. 2024 Feb 27;42(6):1401-1406. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.01.088. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Vaccine. 2024. PMID: 38310015 Review.
Cited by
-
Ally, adversary, or arbitrator? The context-dependent role of eosinophils in vaccination for respiratory viruses and subsequent breakthrough infections.J Leukoc Biol. 2024 Jul 25;116(2):224-243. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae010. J Leukoc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38289826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcome of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection depends on genetic background in female mice.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 23;15(1):10178. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54334-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39580470 Free PMC article.
-
Host immune responses associated with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection result in protection or pathology during reinfection depending on mouse genetic background.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 29:rs.3.rs-3637405. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3637405/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 23;15(1):10178. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54334-7. PMID: 38077015 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Pannus P, Depickère S, Kemlin D, Houben S, Neven KY, Heyndrickx L, et al.. Safety and immunogenicity of a reduced dose of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (REDU-VAC): A single blind, randomized, non-inferiority trial. PLOS Glob Public Heal. 2022;2: e0001308. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0001308 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

