Changes in the expression of mexB, mexY, and oprD in clinical Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates
- PMID: 38199247
- PMCID: PMC10864171
- DOI: 10.2183/pjab.100.006
Changes in the expression of mexB, mexY, and oprD in clinical Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates
Abstract
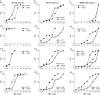
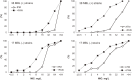
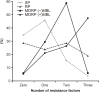
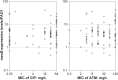
Changes in expression levels of drug efflux pump genes, mexB and mexY, and porin gene oprD in Pseudomonas aeruginosa were investigated in this study. Fifty-five multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa (MDRP) strains were compared with 26 drug-sensitive strains and 21 strains resistant to a single antibiotic. The effect of the efflux inhibitor Phe-Arg-β-naphthylamide on drug susceptibility was determined, and gene expression was quantified using real-time quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. In addition, the levels of metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) and 6'-N-aminoglycoside acetyltransferase [AAC(6')-Iae] were investigated. Efflux pump inhibitor treatment increased the sensitivity to ciprofloxacin, aztreonam, and imipenem in 71%, 73%, and 29% of MDRPs, respectively. MBL and AAC(6')-Iae were detected in 38 (69%) and 34 (62%) MDRP strains, respectively. Meanwhile, 76% of MDRP strains exhibited more than 8-fold higher mexY expression than the reference strain PAO1. Furthermore, 69% of MDRP strains expressed oprD at levels less than 0.01-fold of those in PAO1. These findings indicated that efflux pump inhibitors in combination with ciprofloxacin or aztreonam might aid in treating MDRP infections.
Keywords: Phe-Arg-β-naphthylamide; aminoglycoside acetyltransferase; metallo-β-lactamase; multidrug efflux pumps; multidrug resistance.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Carbapenem resistance mechanisms in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: alterations of porin OprD and efflux proteins do not fully explain resistance patterns observed in clinical isolates.APMIS. 2005 Mar;113(3):187-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2005.apm1130306.x. APMIS. 2005. PMID: 15799762
-
MexXY Multidrug Efflux System Is More Frequently Overexpressed in Ciprofloxacin Resistant French Clinical Isolates Compared to Hospital Environment Ones.Front Microbiol. 2019 Feb 26;10:366. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00366. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30863391 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of efflux pump MexAB-OprM and OprD of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from clinical samples using qRT-PCR.Arch Iran Med. 2015 Feb;18(2):102-8. Arch Iran Med. 2015. PMID: 25644798
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa carbapenem resistance mechanisms in Spain: impact on the activity of imipenem, meropenem and doripenem.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011 Sep;66(9):2022-7. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr232. Epub 2011 Jun 8. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21653605
-
Overexpression of AmpC and efflux pumps in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from bloodstream infections: prevalence and impact on resistance in a Spanish multicenter study.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 May;55(5):1906-11. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01645-10. Epub 2011 Feb 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21357294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hakki M., Limaye A.P., Kim H.W., Kirby K.A., Corey L., Boeckh M. (2007) Invasive Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: high rate of recurrence and mortality after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 39, 687–693. - PubMed
-
- Wagner V.E., Iglewski B.H. (2008) P. aeruginosa biofilms in CF infection. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 35, 124–134. - PubMed
-
- Nikaido H. (1994) Prevention of drug access to bacterial targets: permeability barriers and active efflux. Science 264, 382–388. - PubMed
-
- Schweizer H.P. (2003) Efflux as a mechanism of resistance to antimicrobials in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and related bacteria: unanswered questions. Genet. Mol. Res. 2, 48–62. - PubMed
-
- Pagès J.M., James C.E., Winterhalter M. (2008) The porin and the permeating antibiotic: a selective diffusion barrier in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 893–903. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

