PTP1B mediates the inhibitory effect of MFGE8 on insulin signaling through the β5 integrin
- PMID: 38199575
- PMCID: PMC10850974
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105631
PTP1B mediates the inhibitory effect of MFGE8 on insulin signaling through the β5 integrin
Abstract
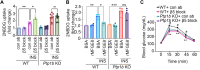
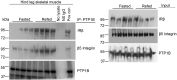
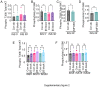
Integrins are cell adhesion receptors that dimerize to mediate cell-cell interactions and regulate processes, including proliferation, inflammation, and tissue repair. The role of integrins in regulating insulin signaling is incompletely understood. We have previously shown that binding of the integrin ligand milk fat globule epidermal growth factor like 8 (MFGE8) to the αvβ5 integrin promotes termination of insulin receptor signaling in mice. Upon ligation of MFGE8, integrin β5 complexes with the insulin receptor beta (IRβ) in skeletal muscle, resulting in dephosphorylation of IRβ and reduction of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake. Here, we investigate the mechanism by which the interaction between β5 and IRβ impacts IRβ phosphorylation status. We show in in vitro and in vivo in skeletal muscle in mice that antibody-mediated blockade of the β5 integrin inhibits and recombinant MFGE8 promotes PTP1B binding to and dephosphorylation of IRβ resulting in increased or reduced insulin-stimulated glucose uptake, respectively. The β5-PTP1B complex is recruited by MFGE8 to IRβ leading to termination of canonical insulin signaling. β5 blockade enhances insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in wildtype but not Ptp1b KO mice indicating that PTP1B functions downstream of MFGE8 in modulating insulin receptor signaling. Furthermore, in a human cohort, we report serum MFGE8 levels correlate with indices of insulin resistance. These data provide mechanistic insights into the role of MFGE8 and β5 in regulating insulin signaling.
Keywords: MFGE8; insulin recpetor; insulin resistance; insulin signaling; integrins.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures





Update of
-
MFGE8 inhibits insulin signaling through PTP1B.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 1:2023.05.30.542928. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.30.542928. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Biol Chem. 2024 Feb;300(2):105631. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105631. PMID: 37398282 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

