E. hellem Ser/Thr protein phosphatase PP1 targets the DC MAPK pathway and impairs immune functions
- PMID: 38199846
- PMCID: PMC10781585
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202302375
E. hellem Ser/Thr protein phosphatase PP1 targets the DC MAPK pathway and impairs immune functions
Abstract
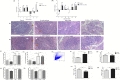
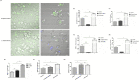
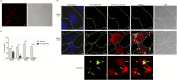
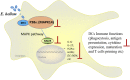
Microsporidia are difficult to be completely eliminated once infected, and the persistence disrupts host cell functions. Here in this study, we aimed to elucidate the impairing effects and consequences of microsporidia on host DCs. Enterocytozoon hellem, one of the most commonly diagnosed zoonotic microsporidia species, was applied. In vivo models demonstrated that E. hellem-infected mice were more susceptible to further pathogenic challenges, and DCs were identified as the most affected groups of cells. In vitro assays revealed that E. hellem infection impaired DCs' immune functions, reflected by down-regulated cytokine expressions, lower extent of maturation, phagocytosis ability, and antigen presentations. E. hellem infection also detained DCs' potencies to prime and stimulate T cells; therefore, host immunities were disrupted. We found that E. hellem Ser/Thr protein phosphatase PP1 directly interacts with host p38α (MAPK14) to manipulate the p38α(MAPK14)/NFAT5 axis of the MAPK pathway. Our study is the first to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of the impairing effects of microsporidia on host DCs' immune functions. The emergence of microsporidiosis may be of great threat to public health.
© 2024 Bao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Animal reservoirs of human virulent microsporidian species].Wiad Parazytol. 2009;55(1):63-5. Wiad Parazytol. 2009. PMID: 19579789 Polish.
-
Characterization of a Murine Model for Encephalitozoon hellem Infection after Dexamethasone Immunosuppression.Microorganisms. 2020 Nov 29;8(12):1891. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8121891. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33260440 Free PMC article.
-
Encephalitozoon hellem Infection Promotes Monocytes Extravasation.Pathogens. 2022 Aug 15;11(8):914. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11080914. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36015036 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro cultivation of microsporidia of clinical importance.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002 Jul;15(3):401-13. doi: 10.1128/CMR.15.3.401-413.2002. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12097248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential role of MAPK signaling in human dendritic cell maturation and Th1/Th2 engagement.J Dermatol Sci. 2006 Apr;42(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2005.11.004. Epub 2005 Dec 13. J Dermatol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16352421 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
