Strong selection signatures for Aleutian disease tolerance acting on novel candidate genes linked to immune and cellular responses in American mink (Neogale vison)
- PMID: 38200094
- PMCID: PMC10781757
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-51039-7
Strong selection signatures for Aleutian disease tolerance acting on novel candidate genes linked to immune and cellular responses in American mink (Neogale vison)
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Strong selection signatures for Aleutian disease tolerance acting on novel candidate genes linked to immune and cellular responses in American mink (Neogale vison).Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 3;14(1):7842. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57764-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38570580 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
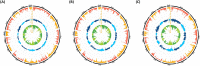
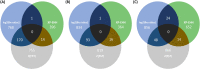
Aleutian disease (AD) is a multi-systemic infectious disease in American mink (Neogale vison) caused by Aleutian mink disease virus (AMDV). This study aimed to identify candidate regions and genes underlying selection for response against AMDV using whole-genome sequence (WGS) data. Three case-control selection signatures studies were conducted between animals (N = 85) producing high versus low antibody levels against AMDV, grouped by counter immunoelectrophoresis (CIEP) test and two enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). Within each study, selection signals were detected using fixation index (FST) and nucleotide diversity (θπ ratios), and validated by cross-population extended haplotype homozygosity (XP-EHH) test. Within- and between-studies overlapping results were then evaluated. Within-studies overlapping results indicated novel candidate genes related to immune and cellular responses (e.g., TAP2, RAB32), respiratory system function (e.g., SPEF2, R3HCC1L), and reproduction system function (e.g., HSF2, CFAP206) in other species. Between-studies overlapping results identified three large segments under strong selection pressure, including two on chromosome 1 (chr1:88,770-98,281 kb and chr1:114,133-120,473) and one on chromosome 6 (chr6:37,953-44,279 kb). Within regions with strong signals, we found novel candidate genes involved in immune and cellular responses (e.g., homologous MHC class II genes, ITPR3, VPS52) in other species. Our study brings new insights into candidate regions and genes controlling AD response.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Aleutian disease: Risk factors and ImmunAD strategy for genetic improvement of tolerance in American mink (Neogale vison).PLoS One. 2024 Jul 18;19(7):e0306135. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306135. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39024380 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of selection signatures for response to Aleutian mink disease virus infection in American mink.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 3;11(1):2944. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82522-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33536540 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and diagnosis of Aleutian disease caused by Aleutian mink disease virus: A literature review with a perspective of genomic breeding for disease control in American mink (Neogale vison).Virus Res. 2023 Oct 15;336:199208. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199208. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 37633597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accuracy of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for quantification of antibodies against Aleutian mink disease virus.J Virol Methods. 2016 Sep;235:144-151. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2016.06.004. Epub 2016 Jun 6. J Virol Methods. 2016. PMID: 27283885
-
Seroprevalence and Molecular Epidemiology of Aleutian Disease in Various Countries during 1972-2021: A Review and Meta-Analysis.Animals (Basel). 2021 Oct 15;11(10):2975. doi: 10.3390/ani11102975. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34679996 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Farid AH. Response of American mink to selection for tolerance to Aleutian mink disease virus. EC Microbiol. 2020;16:110–128.
-
- Newman SJ, Reed A. A national survey for Aleutian disease prevalence in ranch mink herds in Canada. Scientifur. 2006;30:33.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

