MRE11 liberates cGAS from nucleosome sequestration during tumorigenesis
- PMID: 38200309
- PMCID: PMC10794148
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06889-6
MRE11 liberates cGAS from nucleosome sequestration during tumorigenesis
Abstract
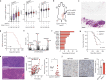
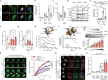
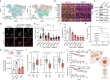
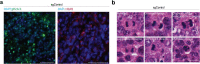
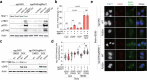
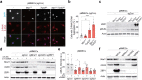
Oncogene-induced replication stress generates endogenous DNA damage that activates cGAS-STING-mediated signalling and tumour suppression1-3. However, the precise mechanism of cGAS activation by endogenous DNA damage remains enigmatic, particularly given that high-affinity histone acidic patch (AP) binding constitutively inhibits cGAS by sterically hindering its activation by double-stranded DNA (dsDNA)4-10. Here we report that the DNA double-strand break sensor MRE11 suppresses mammary tumorigenesis through a pivotal role in regulating cGAS activation. We demonstrate that binding of the MRE11-RAD50-NBN complex to nucleosome fragments is necessary to displace cGAS from acidic-patch-mediated sequestration, which enables its mobilization and activation by dsDNA. MRE11 is therefore essential for cGAS activation in response to oncogenic stress, cytosolic dsDNA and ionizing radiation. Furthermore, MRE11-dependent cGAS activation promotes ZBP1-RIPK3-MLKL-mediated necroptosis, which is essential to suppress oncogenic proliferation and breast tumorigenesis. Notably, downregulation of ZBP1 in human triple-negative breast cancer is associated with increased genome instability, immune suppression and poor patient prognosis. These findings establish MRE11 as a crucial mediator that links DNA damage and cGAS activation, resulting in tumour suppression through ZBP1-dependent necroptosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
G.P.G. is a co-inventor on a patent held by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill on methods for detecting tumour-derived viral DNA in blood (US patent 11,168,373), receives patent licensing fees from and has equity in Naveris, and is the recipient of research funding from Breakpoint Therapeutics and Merck. C.M.P is an equity stockholder and consultant of BioClassifier. C.M.P. is also listed as an inventor on patent applications for the Breast PAM50 Subtyping assay. M.-G.C, R.J.K., C.-C.L., J.A.B., J.A.S., K.F.-S., D.A.S., C.F., C.E.F., A.M.G., L.M.L., S.W.E., Q.W., Y.W., A.Y.H., P.L., Q.Z., R.K.M. and J.E.P. have no competing interests.
Figures

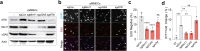
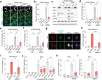
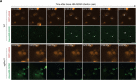

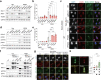


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

