The critically ill older patient with sepsis: a narrative review
- PMID: 38200360
- PMCID: PMC10781658
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-023-01233-7
The critically ill older patient with sepsis: a narrative review
Abstract
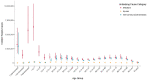
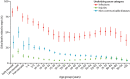
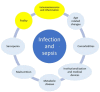
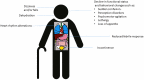
Sepsis is a significant public health concern, particularly affecting individuals above 70 years in developed countries. This is a crucial fact due to the increasing aging population, their heightened vulnerability to sepsis, and the associated high mortality rates. However, the morbidity and long-term outcomes are even more notable. While many patients respond well to timely and appropriate interventions, it is imperative to enhance efforts in identifying, documenting, preventing, and treating sepsis. Managing sepsis in older patients poses greater challenges and necessitates a comprehensive understanding of predisposing factors and a heightened suspicion for diagnosing infections and assessing the risk of sudden deterioration into sepsis. Despite age often being considered an independent risk factor for mortality and morbidity, recent research emphasizes the pivotal roles of frailty, disease severity, and comorbid conditions in influencing health outcomes. In addition, it is important to inquire about the patient's preferences and establish a personalized treatment plan that considers their potential for recovery with quality of life and functional outcomes. This review provides a summary of the most crucial aspects to consider when dealing with an old critically ill patient with sepsis.
Keywords: Infection outcomes; Intensive care; Old; Sepsis; Very old.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have conflicts of interest; both authors have read the current “Instructions to authors” and accept the conditions posed therein. This manuscript is original and has not been and will not be simultaneously submitted elsewhere for publication. None of the material from this study is included in another manuscript, has been published previously, or has been posted on the internet.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

