Organoids derived from patients provide a new opportunity for research and individualized treatment of malignant peritoneal mesothelioma
- PMID: 38200517
- PMCID: PMC10782772
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-023-01901-z
Organoids derived from patients provide a new opportunity for research and individualized treatment of malignant peritoneal mesothelioma
Abstract
Background: Malignant peritoneal mesothelioma (MPM) is an extremely rare and highly invasive tumor. Due to the lack of accurate models that reflect the biological characteristics of primary tumors, studying MPM remains challenging and is associated with an exceedingly unfavorable prognosis. This study was aimed to establish a new potential preclinical model for MPM using patient-derived MPM organoids (MPMOs) and to comprehensively evaluate the practicality of this model in medical research and its feasibility in guiding individualized patient treatment.
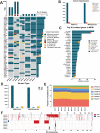
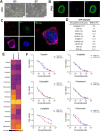
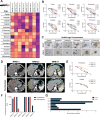
Methods: MPMOs were constructed using tumor tissue from MPM patients. Histopathological analysis and whole genome sequencing (WGS) were employed to determine the ability of MPMOs to replicate the original tumor's genetic and histological characteristics. The subcutaneous and orthotopic xenograft models were employed to assess the feasibility of establishing an in vivo model of MPM. MPMOs were also used to conduct drug screening and compare the results with retrospective analysis of patients after treatment, in order to evaluate the potential of MPMOs in predicting the effectiveness of drugs in MPM patients.
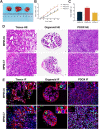
Results: We successfully established a culture method for human MPM organoids using tumor tissue from MPM patients and provided a comprehensive description of the necessary medium components for MPMOs. Pathological examination and WGS revealed that MPMOs accurately represented the histological characteristics and genomic heterogeneity of the original tumors. In terms of application, the success rate of creating subcutaneous and orthotopic xenograft models using MPMOs was 88% and 100% respectively. Drug sensitivity assays demonstrated that MPMOs have different medication responses, and these differences were compatible with the real situation of the patients.
Conclusion: This study presents a method for generating human MPM organoids, which can serve as a valuable research tool and contribute to the advancement of MPM research. Additionally, these organoids can be utilized as a means to evaluate the effectiveness of drug treatments for MPM patients, offering a model for personalized treatment approaches.
Keywords: Drug screen; Malignant peritoneal Mesothelioma; Organoids; Patient-derived organoids (PDO); Patient-derived organoids xenograft (PDOX); Peritoneal orthotopic xenograft; Precision medicine; Primary cell lines; Translational medicine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Establishment and histopathological study of patient-derived xenograft models and primary cell lines of epithelioid malignant peritoneal mesothelioma.Exp Anim. 2021 May 13;70(2):225-235. doi: 10.1538/expanim.20-0119. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Exp Anim. 2021. PMID: 33473097 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment and characterization of patient derived xenograft model of malignant peritoneal mesothelioma in nude mice].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Feb 8;49(2):162-167. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5807.2020.02.011. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32074730 Chinese.
-
Organoids as a Model for Precision Medicine in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Where Are We Today?Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 2;14(15):3758. doi: 10.3390/cancers14153758. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35954422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antitumor effect of novel anti-podoplanin antibody NZ-12 against malignant pleural mesothelioma in an orthotopic xenograft model.Cancer Sci. 2016 Sep;107(9):1198-205. doi: 10.1111/cas.12985. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27294401 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of centralization of care for malignant peritoneal mesothelioma: A historical cohort study from the Dutch mesothelioma expert centers.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2023 Mar;49(3):611-618. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2022.10.003. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36610896 Review.
Cited by
-
Organoids-on-Chips Technology: Unveiling New Perspectives in Rare-Disease Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 4;26(9):4367. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094367. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesothelioma-Associated Fibroblasts Modulate the Response of Mesothelioma Patient-Derived Organoids to Chemotherapy via Interleukin-6.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 14;25(10):5355. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105355. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791392 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-derived tumor organoids: a new avenue for preclinical research and precision medicine in oncology.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Jul;56(7):1531-1551. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01272-5. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38945959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TSC2-mutated perivascular epithelioid cell tumor with partial response to mTOR inhibition: a case report and literature review.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jul 30;16(1):1447. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03270-z. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40739411 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the application of colorectal cancer organoids in precision medicine.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 3;14:1506606. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1506606. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39697234 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chapel DB, Schulte JJ, Absenger G, et al. Malignant peritoneal Mesothelioma: prognostic significance of clinical and pathologic parameters and validation of a nuclear-grading system in a multi-institutional series of 225 cases. Mod Pathol. 2021;34(2):380–395. doi: 10.1038/s41379-020-00688-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2015060911020462/The Clinical Medical Research Center of Peritoneal Cancer of Wuhan
- 2015060911020462/The Clinical Medical Research Center of Peritoneal Cancer of Wuhan
- 2015060911020462/The Clinical Medical Research Center of Peritoneal Cancer of Wuhan
- 2015060911020462/The Clinical Medical Research Center of Peritoneal Cancer of Wuhan
- 2015060911020462/The Clinical Medical Research Center of Peritoneal Cancer of Wuhan
- 2015060911020462/The Clinical Medical Research Center of Peritoneal Cancer of Wuhan
- 2015060911020462/The Clinical Medical Research Center of Peritoneal Cancer of Wuhan
- 2015060911020462/The Clinical Medical Research Center of Peritoneal Cancer of Wuhan
- 2015060911020462/The Clinical Medical Research Center of Peritoneal Cancer of Wuhan
- 320.6750.2023-11-9/The Clinical Research Projects of Wu JiePing Medical Foundation
- 320.6750.2023-11-9/The Clinical Research Projects of Wu JiePing Medical Foundation
- 320.6750.2023-11-9/The Clinical Research Projects of Wu JiePing Medical Foundation
- 320.6750.2023-11-9/The Clinical Research Projects of Wu JiePing Medical Foundation
- 320.6750.2023-11-9/The Clinical Research Projects of Wu JiePing Medical Foundation
- 320.6750.2023-11-9/The Clinical Research Projects of Wu JiePing Medical Foundation
- 320.6750.2023-11-9/The Clinical Research Projects of Wu JiePing Medical Foundation
- 320.6750.2023-11-9/The Clinical Research Projects of Wu JiePing Medical Foundation
- CXPY2022055/Science and Technology Innovation Cultivation Fund of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- CXPY2022055/Science and Technology Innovation Cultivation Fund of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- CXPY2022055/Science and Technology Innovation Cultivation Fund of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- CXPY2022055/Science and Technology Innovation Cultivation Fund of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- CXPY2022055/Science and Technology Innovation Cultivation Fund of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- CXPY2022055/Science and Technology Innovation Cultivation Fund of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- CXPY2022055/Science and Technology Innovation Cultivation Fund of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- CXPY2022055/Science and Technology Innovation Cultivation Fund of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- PTXM2023004/the Medical Science and Technology Innovation Platform Support Project of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- PTXM2023004/the Medical Science and Technology Innovation Platform Support Project of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- PTXM2023004/the Medical Science and Technology Innovation Platform Support Project of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- PTXM2023004/the Medical Science and Technology Innovation Platform Support Project of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- PTXM2023004/the Medical Science and Technology Innovation Platform Support Project of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- PTXM2023004/the Medical Science and Technology Innovation Platform Support Project of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- PTXM2023004/the Medical Science and Technology Innovation Platform Support Project of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- PTXM2023004/the Medical Science and Technology Innovation Platform Support Project of Zhong Nan Hospital of Wuhan University
- 82070302/The National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82070302/The National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

