Influences of Supplementing Selective Members of the Interleukin-6 Cytokine Family on Bovine Oocyte Competency
- PMID: 38200775
- PMCID: PMC10778514
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14010044
Influences of Supplementing Selective Members of the Interleukin-6 Cytokine Family on Bovine Oocyte Competency
Abstract
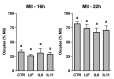
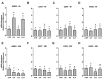
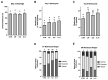
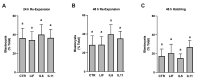
This work explored whether supplementing selective members of the interleukin-6 (IL6) cytokine family during in vitro bovine oocyte maturation affects maturation success, cumulus-oocyte complex (COC) gene expression, fertilization success, and embryo development potential. Human recombinant proteins for IL6, IL11, and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) were supplemented to COCs during the maturation period, then fertilization and embryo culture commenced without further cytokine supplementation. The first study determined that none of these cytokines influenced the rate that oocytes achieved arrest at meiosis II. The second study identified that LIF and IL11 supplementation increases AREG transcript abundance. Supplementation with IL6 supplementation did not affect AREG abundance but reduced HAS2 transcript abundance. Several other transcriptional markers of oocyte competency were not affected by any of the cytokines. The third study determined that supplementing these cytokines during maturation did not influence fertilization success, but either LIF or IL11 supplementation increased blastocyst development. No effect of IL6 supplementation on subsequent blastocyst development was detected. The fourth experiment explored whether each cytokine treatment affects the post-thaw survivability of cryopreserved IVP blastocysts. None of the cytokines supplemented during oocyte maturation produced any positive effects on post-thaw blastocyst re-expansion and hatching. In conclusion, these outcomes implicate IL11 and LIF as potentially useful supplements for improving bovine oocyte competency.
Keywords: cow; cytokine; in vitro embryo production; interleukin; oocyte.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

