Trends in Admissions and Outcomes at a British Wildlife Rehabilitation Centre over a Ten-Year Period (2012-2022)
- PMID: 38200817
- PMCID: PMC10778305
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14010086
Trends in Admissions and Outcomes at a British Wildlife Rehabilitation Centre over a Ten-Year Period (2012-2022)
Abstract
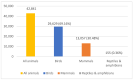
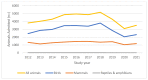
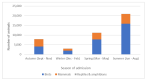
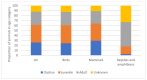
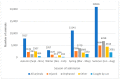
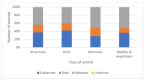
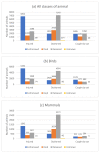
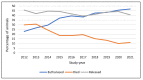
Millions of animals pass through wildlife rehabilitation centres (WRCs) globally each year, some dying in captivity, others euthanised, and some released into the wild. Those caring for these animals are generally well-intentioned, but skills, knowledge, and resources may be limited, potentially compromising animal welfare. WRC databases provide an opportunity to provide an evidence base for treatment and conservation efforts. 42,841 records of animals admitted over a 10-year period to a British WRC were analysed. More birds (69.16%) were admitted than mammals (30.48%) and reptiles and amphibians (0.36%). Most admissions were in the summer (48.8%) and spring (26.0%) months. A total of 9 of the 196 species seen made up 57% of admissions, and hedgehogs were the most common species admitted (14% of all admissions and 20% of mammals). Juvenile animals (35.5%) were admitted more frequently than 'orphans' (26.0%) or adults (26.4%). 'Orphaned' was also the predominant reason for admission (28.3%), followed by 'injured' (25.5%). 42.6% of animals were eventually released back to the wild, 19.2% died in captivity, and 37.2% were euthanised; 1% of outcomes were unknown. The prognosis was better for orphaned animals than for those admitted because of injury. Unexpected natural deaths in captivity were found to decline over the period of study, consistent with improved early triage. These findings can be used to focus veterinary and WRC training and seasonal resources on the species and case types most likely to be successfully rehabilitated and released. The findings also have the potential to contribute to our understanding of anthropogenic impacts, historical and regional variations in ecosystem health, and resultant implications for animal welfare.
Keywords: hedgehog; rehabilitation; rescue; triage; welfare; wildlife.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have read the journal’s policy and have the following competing interests: the author (E.M.) is employee of Capital Veterinary Services Ltd. The other author has no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Miller E.A., editor. Minimum Standards for Wildlife Rehabilitation. 4th ed. National Wildlife Rehabilitators Association and International Wildlife Rehabilitation Council; St. Cloud, MN, USA: 2012. p. 9.
-
- Tribe A., Brown P.R. The role of wildlife rescue groups in the care and rehabilitation of Australian fauna. Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 2000;5:69–85. doi: 10.1080/10871200009359180. - DOI
-
- Englefield B., Blackman S.A., Starling M., McGreevy P.D. A Review of Australian Animal Welfare Legislation, Regulation, Codes of Practice, and Policy, and Their Influence on Stakeholders Caring for Wildlife and the Animals for Whom They Care. Animals. 2019;9:335. doi: 10.3390/ani9060335. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

